Page 112 - DMGT409Basic Financial Management
P. 112
Unit 6: Capital Structure Theory
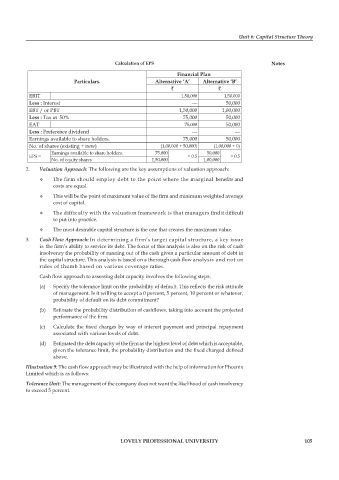
Calculation of EPS Notes
Financial Plan
Particulars. Alternative ‘A’ Alternative ‘B’
` `
EBIT 1,50,000 1,50,000
Less : Interest --- 50,000
EBT / or PBT 1,50,000 1,00,000
Less : Tax at 50% 75,000 50,000
EAT 75,000 50,000
Less : Preference dividend --- ---
Earnings available to share holders. 75,000 50,000
No. of shares (existing + new) (1,00,000 + 50,000) (1,00,000 + 0)
Earnings available to share holders. 75,000 50,000
EPS = = 0.5 = 0.5
No. of equity shares 1,50,000 1,00,000
2. Valuation Approach: The following are the key assumptions of valuation approach:
The firm should employ debt to the point where the marginal benefi ts and
costs are equal.
This will be the point of maximum value of the firm and minimum weighted average
cost of capital.
The difficulty with the valuation framework is that managers find it diffi cult
to put into practice.
The most desirable capital structure is the one that creates the maximum value.
3. Cash Flow Approach: In determining a firm’s target capital structure, a key issue
is the firm’s ability to service its debt. The focus of this analysis is also on the risk of cash
insolvency the probability of running out of the cash given a particular amount of debt in
the capital structure. This analysis is based on a thorough cash flow analysis and not on
rules of thumb based on various coverage ratios.
Cash flow approach to assessing debt capacity involves the following steps:
(a) Specify the tolerance limit on the probability of default. This reflects the risk attitude
of management. Is it willing to accept a 0 percent, 5 percent, 10 percent or whatever,
probability of default on its debt commitment?
(b) Estimate the probability distribution of cashflows, taking into account the projected
performance of the fi rm.
(c) Calculate the fixed charges by way of interest payment and principal repayment
associated with various levels of debt.
(d) Estimated the debt capacity of the firm as the highest level of debt which is acceptable,
given the tolerance limit, the probability distribution and the fixed charged defi ned
above.
Illustration 9: The cash flow approach may be illustrated with the help of information for Phoenix
Limited which is as follows:
Tolerance Unit: The management of the company does not want the likelihood of cash insolvency
to exceed 5 percent.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 105