Page 90 - DCAP406_DCAP_207_Computer Networks
P. 90
Unit 6: Multiplexing
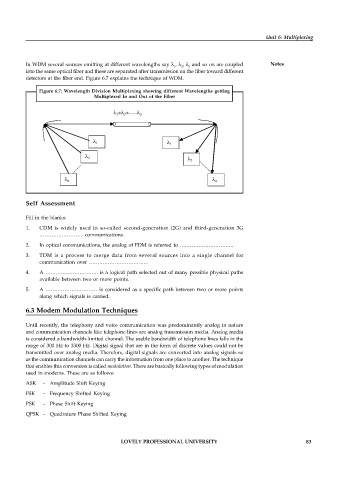
In WDM several sources emitting at different wavelengths say λ , λ , λ and so on are coupled Notes
1 2 3
into the same optical fiber and these are separated after transmission on the fiber toward different
detectors at the fiber end. Figure 6.7 explains the technique of WDM.
Figure 6.7: Wavelength Division Multiplexing showing different Wavelengths getting
Multiplexed In and Out of the Fiber
λ 1 +λ 2 +-----λ n
λ 1 λ 1
λ 2
λ 2
λ n λ n
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. CDM is widely used in so-called second-generation (2G) and third-generation 3G
…………………….. communications.
2. In optical communications, the analog of FDM is referred to …………………………..
3. TDM is a process to merge data from several sources into a single channel for
communication over ……………………………..
4. A …………………………. is a logical path selected out of many possible physical paths
available between two or more points.
5. A ………………………… is considered as a specific path between two or more points
along which signals is carried.
6.3 Modem Modulation Techniques
Until recently, the telephony and voice communication was predominantly analog in nature
and communication channels like telephone lines are analog transmission media. Analog media
is considered a bandwidth-limited channel. The usable bandwidth of telephone lines falls in the
range of 300 Hz to 3300 Hz. Digital signal that are in the form of discrete values could not be
transmitted over analog media. Therefore, digital signals are converted into analog signals so
as the communication channels can carry the information from one place to another. The technique
that enables this conversion is called modulation. There are basically following types of modulation
used in modems. These are as follows:
ASK – Amplitude Shift Keying
FSK – Frequency Shifted Keying
PSK – Phase Shift Keying
QPSK – Quadrature Phase Shifted Keying
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 83