Page 95 - DCAP406_DCAP_207_Computer Networks
P. 95
Computer Networks/Networks
Notes This technique of letting each shift of a wave represent some bit value is phase shift keying. But
the real key is to shift each wave relative to the wave that came before it. PSK describes the
modulation technique that alters the phase of the carrier. Mathematically, it can be represented
as y(t) = f(t) sin(2pfct + j(t)) where jc is phase shift. This method is easier to detect than the
previous one. The receiver has to detect the phase shifts between symbols and not the absolute
phase.
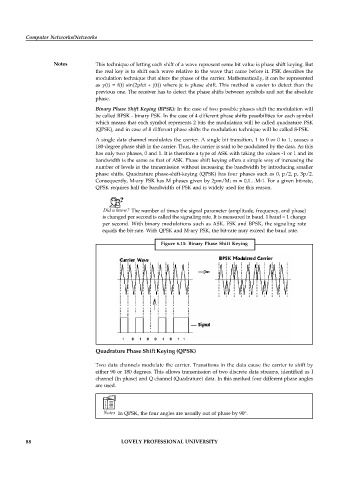
Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): In the case of two possible phases shift the modulation will
be called BPSK - binary PSK. In the case of 4 different phase shifts possibilities for each symbol
which means that each symbol represents 2 bits the modulation will be called quadrature PSK
(QPSK), and in case of 8 different phase shifts the modulation technique will be called 8-PSK.
A single data channel modulates the carrier. A single bit transition, 1 to 0 or 0 to 1, causes a
180-degree phase shift in the carrier. Thus, the carrier is said to be modulated by the data. As this
has only two phases, 0 and 1. It is therefore a type of ASK with taking the values -1 or 1 and its
bandwidth is the same as that of ASK. Phase shift keying offers a simple way of increasing the
number of levels in the transmission without increasing the bandwidth by introducing smaller
phase shifts. Quadrature phase-shift-keying (QPSK) has four phases such as 0, p/2, p, 3p/2.
Consequently, M-ary PSK has M phases given by 2pm/M; m = 0,1…M-1. For a given bit-rate,
QPSK requires half the bandwidth of PSK and is widely used for this reason.
Did u know? The number of times the signal parameter (amplitude, frequency, and phase)
is changed per second is called the signaling rate. It is measured in baud. 1 baud = 1 change
per second. With binary modulations such as ASK, FSK and BPSK, the signaling rate
equals the bit-rate. With QPSK and M-ary PSK, the bit-rate may exceed the baud rate.
Figure 6.11: Binary Phase Shift Keying
Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)
Two data channels modulate the carrier. Transitions in the data cause the carrier to shift by
either 90 or 180 degrees. This allows transmission of two discrete data streams, identified as I
channel (In phase) and Q channel (Quadrature) data. In this method four different phase angles
are used.
Notes In QPSK, the four angles are usually out of phase by 90°.
88 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY