Page 165 - DCAP408_WEB_PROGRAMMING
P. 165
Unit 5: Scripting Language
Notes
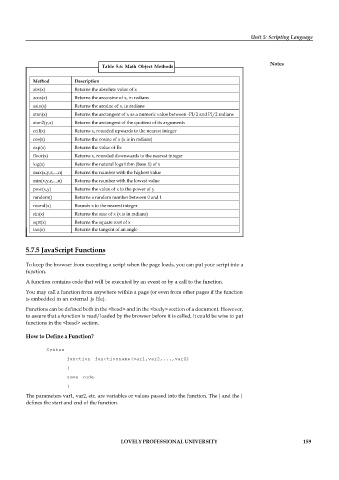
Table 5.6: Math Object Methods
Method Description
abs(x) Returns the absolute value of x
acos(x) Returns the arccosine of x, in radians
asin(x) Returns the arcsine of x, in radians
atan(x) Returns the arctangent of x as a numeric value between -PI/2 and PI/2 radians
atan2(y,x) Returns the arctangent of the quotient of its arguments
ceil(x) Returns x, rounded upwards to the nearest integer
cos(x) Returns the cosine of x (x is in radians)
exp(x) Returns the value of Ex
floor(x) Returns x, rounded downwards to the nearest integer
log(x) Returns the natural logarithm (base E) of x
max(x,y,z,...,n) Returns the number with the highest value
min(x,y,z,...,n) Returns the number with the lowest value
pow(x,y) Returns the value of x to the power of y
random() Returns a random number between 0 and 1
round(x) Rounds x to the nearest integer
sin(x) Returns the sine of x (x is in radians)
sqrt(x) Returns the square root of x
tan(x) Returns the tangent of an angle
5.7.5 JavaScript Functions
To keep the browser from executing a script when the page loads, you can put your script into a
function.
A function contains code that will be executed by an event or by a call to the function.
You may call a function from anywhere within a page (or even from other pages if the function
is embedded in an external .js file).
Functions can be defined both in the <head> and in the <body> section of a document. However,
to assure that a function is read/loaded by the browser before it is called, it could be wise to put
functions in the <head> section.
How to Define a Function?
Syntax
function functionname(var1,var2,...,varX)
{
some code
}
The parameters var1, var2, etc. are variables or values passed into the function. The { and the }
defines the start and end of the function.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 159