Page 34 - DCAP408_WEB_PROGRAMMING
P. 34
Web Programming
Notes
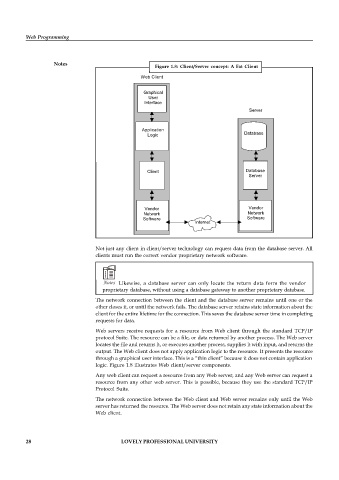
Figure 1.8: Client/Server concept: A Fat Client
Web Client
Graphical
User
Interface
Server
Application Database
Logic
Client Database
Server
Vendor Vendor
Network Network
Software Software
Internet
Not just any client in client/server technology can request data from the database server. All
clients must run the correct vendor proprietary network software.
Notes Likewise, a database server can only locate the return data form the vendor
proprietary database, without using a database gateway to another proprietary database.
The network connection between the client and the database server remains until one or the
other closes it, or until the network fails. The database server retains state information about the
client for the entire lifetime for the connection. This saves the database server time in completing
requests for data.
Web servers receive requests for a resource from Web client through the standard TCP/IP
protocol Suite. The resource can be a file, or data returned by another process. The Web server
locates the file and returns it, or executes another process, supplies it with input, and returns the
output. The Web client does not apply application logic to the resource. It presents the resource
through a graphical user interface. This is a “thin client” because it does not contain application
logic. Figure 1.8 illustrates Web client/server components.
Any web client can request a resource from any Web server, and any Web server can request a
resource from any other web server. This is possible, because they use the standard TCP/IP
Protocol Suite.
The network connection between the Web client and Web server remains only until the Web
server has returned the resource. The Web server does not retain any state information about the
Web client.
28 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY