Page 91 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 91
Data Structure
5.3.2 Doubly-Linked List
Doubly-linked list contains two pointers for each node in the list. The first pointer points to the next
element and the second pointer points to the previous element. The previous pointer for the HEAD
node points to NULL and the next pointer for the last node points to NULL. Doubly-linked list is also
known as a two-way list as both forward and backward traversal is possible.
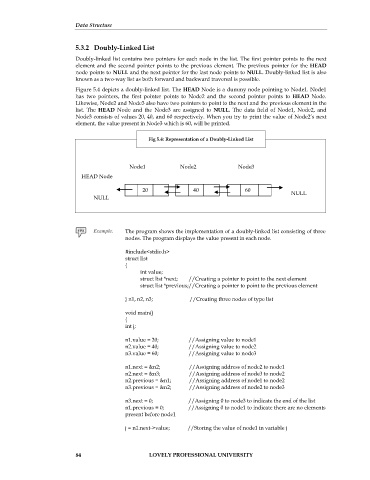
Figure 5.4 depicts a doubly-linked list. The HEAD Node is a dummy node pointing to Node1. Node1
has two pointers, the first pointer points to Node2 and the second pointer points to HEAD Node.
Likewise, Node2 and Node3 also have two pointers to point to the next and the previous element in the
list. The HEAD Node and the Node3 are assigned to NULL. The data field of Node1, Node2, and
Node3 consists of values 20, 40, and 60 respectively. When you try to print the value of Node2’s next
element, the value present in Node3 which is 60, will be printed.
Fig 5.4: Representation of a Doubly-Linked List
Node1 Node2 Node3
HEAD Node
20 40 60
NULL NULL
The program shows the implementation of a doubly-linked list consisting of three
nodes. The program displays the value present in each node.
#include<stdio.h>
struct list
{
int value;
struct list *next; //Creating a pointer to point to the next element
struct list *previous;//Creating a pointer to point to the previous element
} n1, n2, n3; //Creating three nodes of type list
void main()
{
int j;
n1.value = 20; //Assigning value to node1
n2.value = 40; //Assigning value to node2
n3.value = 60; //Assigning value to node3
n1.next = &n2; //Assigning address of node2 to node1
n2.next = &n3; //Assigning address of node3 to node2
n2.previous = &n1; //Assigning address of node1 to node2
n3.previous = &n2; //Assigning address of node2 to node3
n3.next = 0; //Assigning 0 to node3 to indicate the end of the list
n1.previous = 0; //Assigning 0 to node1 to indicate there are no elements
present before node1
j = n1.next->value; //Storing the value of node1 in variable j
84 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY