Page 94 - DCAP407_DATA_STRUCTURE
P. 94
Unit 5: Introduction to Linked List
Write a simple circular linked list program to accept the elements from the user and
store it in a list.
5.3.4 Circular Doubly-Linked List
In a circular doubly-linked list, the previous pointer of the first node and the next pointer of the last
node point to the HEAD node. The HEAD node can have a dummy data or it can store the total number
of nodes present in the list.
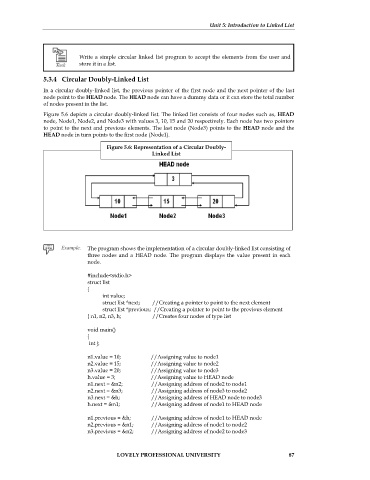
Figure 5.6 depicts a circular doubly-linked list. The linked list consists of four nodes such as, HEAD
node, Node1, Node2, and Node3 with values 3, 10, 15 and 20 respectively. Each node has two pointers
to point to the next and previous elements. The last node (Node3) points to the HEAD node and the
HEAD node in turn points to the first node (Node1).
Figure 5.6: Representation of a Circular Doubly-
Linked List
The program shows the implementation of a circular doubly-linked list consisting of
three nodes and a HEAD node. The program displays the value present in each
node.
#include<stdio.h>
struct list
{
int value;
struct list *next; //Creating a pointer to point to the next element
struct list *previous; //Creating a pointer to point to the previous element
} n1, n2, n3, h; //Creates four nodes of type list
void main()
{
int j;
n1.value = 10; //Assigning value to node1
n2.value = 15; //Assigning value to node2
n3.value = 20; //Assigning value to node3
h.value = 3; //Assigning value to HEAD node
n1.next = &n2; //Assigning address of node2 to node1
n2.next = &n3; //Assigning address of node3 to node2
n3.next = &h; //Assigning address of HEAD node to node3
h.next = &n1; //Assigning address of node1 to HEAD node
n1.previous = &h; //Assigning address of node1 to HEAD node
n2.previous = &n1; //Assigning address of node1 to node2
n3.previous = &n2; //Assigning address of node2 to node3
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 87