Page 6 - DCAP504_Computer Graphics
P. 6
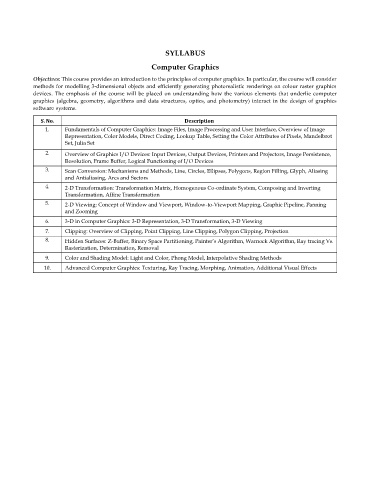
SYLLABUS
Computer Graphics
Objectives: This course provides an introduction to the principles of computer graphics. In particular, the course will consider
methods for modelling 3-dimensional objects and efficiently generating photorealistic renderings on colour raster graphics
devices. The emphasis of the course will be placed on understanding how the various elements that underlie computer
graphics (algebra, geometry, algorithms and data structures, optics, and photometry) interact in the design of graphics
software systems.
S. No. Description
1. Fundamentals of Computer Graphics: Image Files, Image Processing and User Interface, Overview of Image
Representation, Color Models, Direct Coding, Lookup Table, Setting the Color Attributes of Pixels, Mandelbrot
Set, Julia Set
2. Overview of Graphics I/O Devices: Input Devices, Output Devices, Printers and Projectors, Image Persistence,
Resolution, Frame Buffer, Logical Functioning of I/O Devices
3. Scan Conversion: Mechanisms and Methods, Line, Circles, Ellipses, Polygons, Region Filling, Glyph, Aliasing
and Antialiasing, Arcs and Sectors
4. 2-D Transformation: Transformation Matrix, Homogenous Co-ordinate System, Composing and Inverting
Transformation, Affine Transformation
5. 2-D Viewing: Concept of Window and Viewport, Window-to-Viewport Mapping, Graphic Pipeline, Panning
and Zooming
6. 3-D in Computer Graphics: 3-D Representation, 3-D Transformation, 3-D Viewing
7. Clipping: Overview of Clipping, Point Clipping, Line Clipping, Polygon Clipping, Projection
8. Hidden Surfaces: Z-Buffer, Binary Space Partitioning, Painter’s Algorithm, Warnock Algorithm, Ray tracing Vs.
Rasterization, Determination, Removal
9. Color and Shading Model: Light and Color, Phong Model, Interpolative Shading Methods
10. Advanced Computer Graphics: Texturing, Ray Tracing, Morphing, Animation, Additional Visual Effects