Page 223 - DMTH201_Basic Mathematics-1
P. 223
Basic Mathematics – I
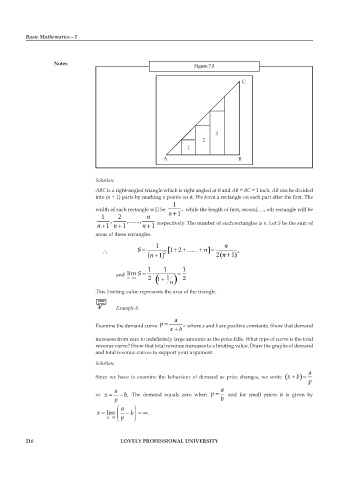
Notes Figure 7.5
C
3
2
1
A B
Solution:
ABC is a right-angled triangle which is right angled at B and AB = BC = 1 inch. AB can be divided
into (n + 1) parts by marking n points on it. We form a rectangle on each part after the first. The
width of each rectangle will be while the length of first, second, ..., nth rectangle will be
respectively. The number of such rectangles is n. Let S be the sum of
areas of these rectangles.
∴
and
This limiting value represents the area of the triangle.
Example 8.
Examine the demand curve where a and b are positive constants. Show that demand
increases from zero to indefinitely large amounts as the price falls. What type of curve is the total
revenue curve? Show that total revenue increases to a limiting value. Draw the graphs of demand
and total revenue curves to support your argument.
Solution:
Since we have to examine the behaviour of demand as price changes, we write
or The demand equals zero when and for small prices it is given by
216 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY