Page 140 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 140
Unit 9: Cost Concepts
Notes
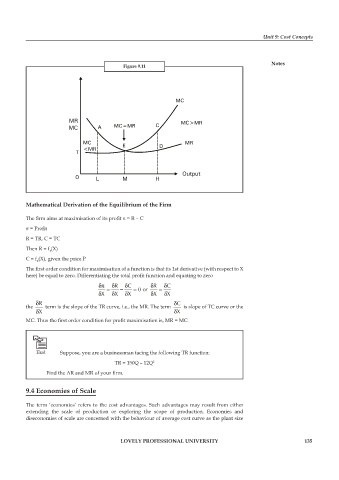
Figure 9.11
Mathematical Derivation of the Equilibrium of the Firm
The firm aims at maximisation of its profi t π = R – C
π = Profi t
R = TR, C = TC
Then R = f (X)
1
C = f (X), given the price P
2
The first order condition for maximisation of a function is that its 1st derivative (with respect to X
here) be equal to zero. Differentiating the total profit function and equating to zero
δπ = δR − δC = 0 or δR = δC
δX δX δX δX δX
δR δC
the term is the slope of the TR curve, i.e., the MR. The term is slope of TC curve or the
δX δX
MC. Thus the first order condition for profit maximisation is, MR = MC.
Task Suppose, you are a businessman facing the following TR function:
TR = 150Q – 12Q 2
Find the AR and MR of your fi rm.
9.4 Economies of Scale
The term ‘economies’ refers to the cost advantages. Such advantages may result from either
extending the scale of production or exploring the scope of production. Economies and
diseconomies of scale are concerned with the behaviour of average cost curve as the plant size
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 135