Page 219 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 219
Micro Economics
Notes companies would be multiproduct, multisectoral, multiregional and multinational. What
implications can this change in the market structure have on the functioning of companies?
What will be the impact on profi tability?
Decorative paints
Industrial paints
Others
27% Asian Paints Others Asian Paints
37% Jenson &
13% 15%
Nichoison
8%
Jenson &
Nichoison
6% ICI India
Goodlass 8%
ICI India Nerolac Goodlass
8% 11% Berger Paints Nerolac
11%
Berger Paints 45%
11%
The emerging mesoeconomic industry structures, apart from indicating the relatively small
number of players, may cover even the differentiated product manufacturers such as the
paints. The existence of mesoeconomic structures could be seen from the concentration
ratios (market shares) of the dominant companies.
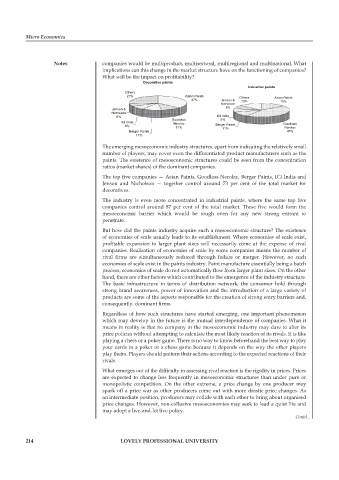
The top five companies — Asian Paints, Goodlass Nerolac, Berger Paints, ICI India and
Jenson and Nicholson — together control around 73 per cent of the total market for
decoratives.
The industry is even more concentrated in industrial paints, where the same top fi ve
companies control around 87 per cent of the total market. These five would form the
mesoeconomic barrier which would be tough even for any new strong entrant to
penetrate.
But how did the paints industry acquire such a mesoeconomic structure? The existence
of economies of scale usually leads to its establishment. Where economies of scale exist,
profitable expansion to larger plant sizes will necessarily come at the expense of rival
companies. Realisation of economies of scale by some companies means the number of
rival firms are simultaneously reduced through failure or merger. However, no such
economies of scale exist in the paints industry. Paint manufacture essentially being a batch
process, economies of scale do not automatically flow from larger plant sizes. On the other
hand, there are other factors which contributed to the emergence of the industry structure.
The basic infrastructure in terms of distribution network, the consumer hold through
strong brand awareness, power of innovation and the introduction of a large variety of
products are some of the aspects responsible for the creation of strong entry barriers and,
consequently, dominant fi rms.
Regardless of how such structures have started emerging, one important phenomenon
which may develop in the future is the mutual interdependence of companies. What it
means in reality is that no company in the mesoeconomic industry may dare to alter its
price policies without attempting to calculate the most likely reaction of its rivals. It is like
playing a chess or a poker game. There is no way to know beforehand the best way to play
your cards in a poker or a chess game because it depends on the way the other players
play theirs. Players should pattern their actions according to the expected reactions of their
rivals.
What emerges out of the difficulty in assessing rival reaction is the rigidity in prices. Prices
are expected to change less frequently in mesoeconomic structures than under pure or
monopolistic competition. On the other extreme, a price change by one producer may
spark off a price war as other producers come out with more drastic price changes. As
an intermediate position, producers may collide with each other to bring about organised
price changes. However, non-collusive mesoeconomies may seek to lead a quiet life and
may adopt a live-and-let live policy.
Contd...
214 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY