Page 38 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 38
Unit 3: Supply and Market Equilibrium
Notes
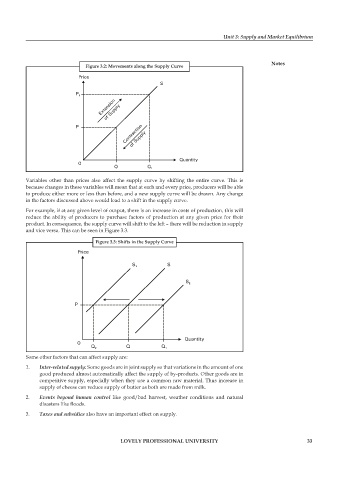
Figure 3.2: Movements along the Supply Curve
Variables other than prices also affect the supply curve by shifting the entire curve. This is
because changes in these variables will mean that at each and every price, producers will be able
to produce either more or less than before, and a new supply curve will be drawn. Any change
in the factors discussed above would lead to a shift in the supply curve.
For example, if at any given level of output, there is an increase in costs of production, this will
reduce the ability of producers to purchase factors of production at any given price for their
product. In consequence, the supply curve will shift to the left – there will be reduction in supply
and vice versa. This can be seen in Figure 3.3.
Figure 3.3: Shifts in the Supply Curve
Some other factors that can affect supply are:
1. Inter-related supply: Some goods are in joint supply so that variations in the amount of one
good produced almost automatically affect the supply of by-products. Other goods are in
competitive supply, especially when they use a common raw material. Thus increase in
supply of cheese can reduce supply of butter as both are made from milk.
2. Events beyond human control like good/bad harvest, weather conditions and natural
disasters like fl oods.
3. Taxes and subsidies also have an important effect on supply.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 33