Page 39 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 39
Micro Economics
Notes 3.4 Market Equilibrium
Price is determined in a free market by the interaction of supply and demand. We can underline
three dynamic laws of supply and demand.
1. When quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied, prices tend to rise; when
quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded, prices tend to fall.
2. In a market, larger the difference between quantity supplied and quantity demanded, the
greater the pressure on prices to rise (if there is excess demand) or fall (if there is excess
supply).
3. When quantity supplied equals quantity demanded, prices have no tendency to change.
Price theory answers the question of interaction of demand and supply to determine price in a
competitive market. Let’s see an example, given in table.
Table 3.1: Market Supply and Demand for Commodity X
Price of Com- Total Quantity Supplied Total Quantity Surplus or Shortage
modity per Month Demanded per Month
5 12,000 2,000 +10,000
4 10,000 4,000 +6,000
3 7,000 7,000 0
2 4,000 11,000 –7,000
1 1,000 16,000 –15,000
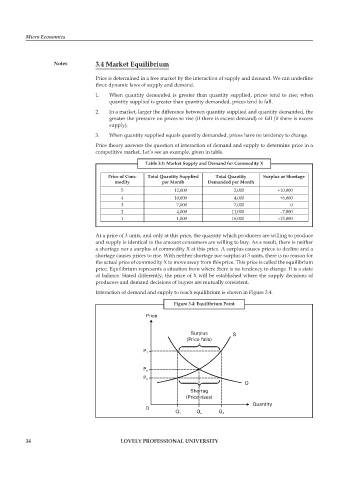
At a price of 3 units, and only at this price, the quantity which producers are willing to produce
and supply is identical to the amount consumers are willing to buy. As a result, there is neither
a shortage nor a surplus of commodity X at this price. A surplus causes prices to decline and a
shortage causes prices to rise. With neither shortage nor surplus at 3 units, there is no reason for
the actual price of commodity X to move away from this price. This price is called the equilibrium
price. Equilibrium represents a situation from where there is no tendency to change. It is a state
of balance. Stated differently, the price of X will be established where the supply decisions of
producers and demand decisions of buyers are mutually consistent.
Interaction of demand and supply to reach equilibrium is shown in Figure 3.4.
Figure 3.4: Equilibrium Point
34 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY