Page 153 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 153
Unit 8: Financial Statements
2 Revenue Expenditure: When expenditure is done for a short period (less than one year) and Notes
for the regular operation of business, it is termed as revenue expenditure. Their benefits
are taken by the business in the current period only. For example:
(a) Expenses incurred during the normal course of business – as salaries of the staff, fuel
and electricity used for the running of machinery and cost of sales.
(b) Expenses for the maintenance of the assets – repairs of machinery.
(c) Wear and tear and obsolescence of the assets and decrease in the value of assets.
3 Deferred Revenue Expenditure: When revenue expenditure is done for the benefit of two or
three years, it is termed as deferred revenue expenditure. For example, cost of heavy
campaign of advertisement, preliminary expenses, etc. The benefit of such type of
expenditure is enjoyed by the company for a number of years. Therefore, the entire amount
of such expenditure is not transferred to the profit & loss account of a year. The entire
amount of such expenditure is divided by a period of time (no. of years in which the
benefit of such expenditure will be enjoyed). The dividend received in written off by
transferring into profit & loss account and the unwritten off portion of the expenditure is
shown in the balance sheet as a fictitious asset.
8.3.2 Classification of Receipts
As distinction is made between the capital expenditure and revenue expenditure, similarly to
calculate the accurate profits or loss of the business distinction between the capital receipt and
revenue receipts is done. Therefore, these words should be clearly understood.
1. Capital Receipts: Capital receipts include the sale of fixed assets, long-term investments,
issue of share capital, debentures and loan raised. Capital receipts are different from the
capital profits or loss. The entire amount from the sale of assets is called capital receipts
and the difference of sale proceeds and cost of assets is capital profit or loss.
2. Revenue Receipts: Receipts which are obtained during the normal course of business are
called revenue receipts. In other words the receipts which are not capital receipts are
revenue receipts as sale of goods. Revenue receipts are different from revenue profits or
loss. For example, goods worth 5,000 are sold at 6,000. Here, the entire sale of 6,000
will be revenue receipts and the revenue profit will be 1,000 only.
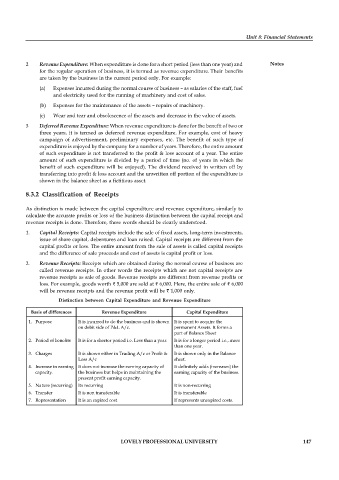
Distinction between Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure
Basis of differences Revenue Expenditure Capital Expenditure
1. Purpose It is incurred to do the business and is shown It is spent to acquire the
on debit side of P&L A/c. permanent Assets. It forms a
part of Balance Sheet
2. Period of benefits It is for a shorter period i.e. Less than a year. It is for a longer period i.e., more
than one year.
3. Charges It is shown either in Trading A/c or Profit & It is shown only in the Balance
Loss A/c sheet.
4. Increase in earning It does not increase the earning capacity of It definitely adds (increases) the
capacity. the business but helps in maintaining the earning capacity of the business.
present profit earning capacity.
5. Nature (recurring) Its recurring It is non-recurring
6. Transfer It is non transferable It is transferable
7. Representation It is an expired cost If represents unexpired costs.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 147