Page 231 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 231
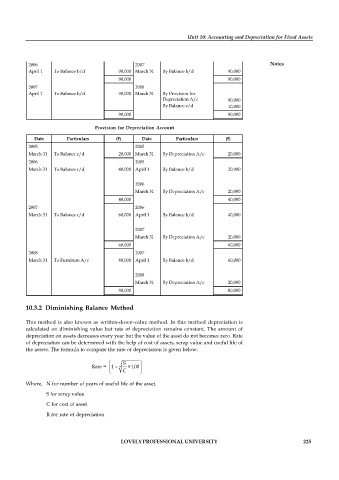
Date Particulars ( ) Date Particulars ( )
2004 2005
April 1 To Bank A/c 90,000 March 31 By Balance c/d 90,000
90,000 90,000
Unit 10: Accounting and Depreciation for Fixed Assets
2005 2006
April 1 To Balance b/d 90,000 March 31 By Balance c/d 90,000
90,000 90,000
2006 2007 Notes
April 1 To Balance b/d 90,000 March 31 By Balance b/d 90,000
90,000 90,000
2007 2008
April 1 To Balance b/d 90,000 March 31 By Provision for
Depreciation A/c 80,000
By Balance c/d 10,000
90,000 90,000
Provision for Depreciation Account
Date Particulars ( ) Date Particulars ( )
2005 2005
March 31 To Balance c/d 20,000 March 31 By Depreciation A/c 20,000
2006 2005
March 31 To Balance c/d 40,000 April 1 By Balance b/d 20,000
2006
March 31 By Depreciation A/c 20,000
40,000 40,000
2007 2006
March 31 To Balance c/d 60,000 April 1 By Balance b/d 40,000
2007
March 31 By Depreciation A/c 20,000
60,000 60,000
2008 2007
March 31 To Furniture A/c 80,000 April 1 By Balance b/d 60,000
2008
March 31 By Depreciation A/c 20,000
80,000 80,000
10.3.2 Diminishing Balance Method
This method is also known as written-down-value method. In this method depreciation is
calculated on diminishing value but rate of depreciation remains constant. The amount of
depreciation on assets decreases every year but the value of the asset do not becomes zero. Rate
of depreciation can be determined with the help of cost of assets, scrap value and useful life of
the assets. The formula to compute the rate of depreciation is given below:
æ S ö
Rate = 1 – n C × 100 ÷ ø
ç
è
Where, N for number of years of useful life of the asset.
S for scrap value
C for cost of asset
R for rate of depreciation
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 225