Page 26 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 26
Financial Accounting
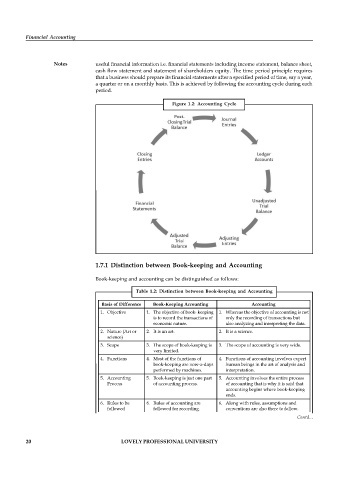
Notes useful financial information i.e. financial statements including income statement, balance sheet,
cash flow statement and statement of shareholders equity. The time period principle requires
that a business should prepare its financial statements after a specified period of time, say a year,
a quarter or on a monthly basis. This is achieved by following the accounting cycle during each
period.
Figure 1.2: Accounting Cycle
1.7.1 Distinction between Book-keeping and Accounting
Book-keeping and accounting can be distinguished as follows:
Table 1.2: Distinction between Book-keeping and Accounting
Basis of Difference Book-Keeping Accounting Accounting
1. Objective 1. The objective of book- keeping 1. Whereas the objective of accounting is not
is to record the transactions of only the recording of transactions but
economic nature. also analyzing and interpreting the data.
2. Nature (Art or 2. It is an art. 2. It is a science.
science)
3. Scope 3. The scope of book-keeping is 3. The scope of accounting is very wide.
very limited.
4. Functions 4. Most of the functions of 4. Functions of accounting involves expert
book-keeping are now-a-days human beings in the art of analysis and
performed by machines. interpretation.
5. Accounting 5. Book-keeping is just one part 5. Accounting involves the entire process
Process of accounting process. of accounting that is why it is said that
accounting begins where book-keeping
ends.
6. Rules to be 6. Rules of accounting are 6. Along with rules, assumptions and
followed followed for recording. conventions are also there to follow.
7. Net Results 7. Net results of the business 7. Whereas accounting is used to find out
Contd...
Profit or loss cannot be known from net results of the business.
book-keeping.
8. Time 8. Transactions are immediately 8. Transactions are generally recorded
20 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY after a gap of time or at the end of a
recorded.
financial year.