Page 236 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 236
Unit 11: Analysis of Time Series
Solution: Notes
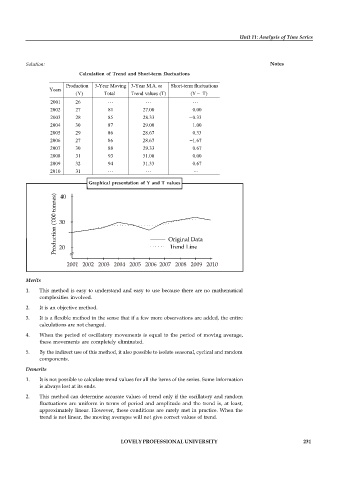
Calculation of Trend and Short-term fluctuations
Production 3-Year Moving 3-Year M.A. or Short-term fluctuations
Years
(Y) Total Trend values (T) (Y T)
2001 26
2002 27 81 27.00 0.00
2003 28 85 28.33 0.33
2004 30 87 29.00 1.00
2005 29 86 28.67 0.33
2006 27 86 28.67 1.67
2007 30 88 29.33 0.67
2008 31 93 31.00 0.00
2009 32 94 31.33 0.67
2010 31
Graphical presentation of Y and T values
2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010
Merits
1. This method is easy to understand and easy to use because there are no mathematical
complexities involved.
2. It is an objective method.
3. It is a flexible method in the sense that if a few more observations are added, the entire
calculations are not changed.
4. When the period of oscillatory movements is equal to the period of moving average,
these movements are completely eliminated.
5. By the indirect use of this method, it also possible to isolate seasonal, cyclical and random
components.
Demerits
1. It is not possible to calculate trend values for all the items of the series. Some information
is always lost at its ends.
2. This method can determine accurate values of trend only if the oscillatory and random
fluctuations are uniform in terms of period and amplitude and the trend is, at least,
approximately linear. However, these conditions are rarely met in practice. When the
trend is not linear, the moving averages will not give correct values of trend.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 231