Page 178 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 178
Unit 10: Theories of Inflation
Thus, cost push inflation occurs due to non-wage factors also. For instance, monopolistic or Notes
oligopolistic firms often attempt to maintain their profit margins steady by raising the prices of
their products in proportion to the rise in other cost elements. Such a cost push inflation is
sometimes called “mark-up” inflation.
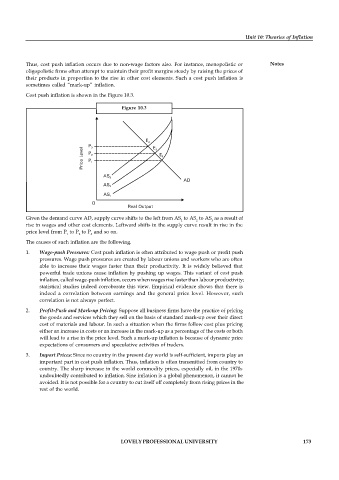
Cost push inflation is shown in the Figure 10.3.
Figure 10.3
Given the demand curve AD, supply curve shifts to the left from AS to AS to AS as a result of
1 2 3
rise in wages and other cost elements. Leftward shifts in the supply curve result in rise in the
price level from P to P to P and so on.
1 2 3
The causes of such inflation are the following.
1. Wage-push Pressures: Cost push inflation is often attributed to wage push or profit push
pressures. Wage push pressures are created by labour unions and workers who are often
able to increase their wages faster than their productivity. It is widely believed that
powerful trade unions cause inflation by pushing up wages. This variant of cost push
inflation, called wage-push inflation, occurs when wages rise faster than labour productivity;
statistical studies indeed corroborate this view. Empirical evidence shows that there is
indeed a correlation between earnings and the general price level. However, such
correlation is not always perfect.
2. Profit-Push and Mark-up Pricing: Suppose all business firms have the practice of pricing
the goods and services which they sell on the basis of standard mark-up over their direct
cost of materials and labour. In such a situation when the firms follow cost plus pricing
either an increase in costs or an increase in the mark-up as a percentage of the costs or both
will lead to a rise in the price level. Such a mark-up inflation is because of dynamic price
expectations of consumers and speculative activities of traders.
3. Import Prices: Since no country in the present day world is self-sufficient, imports play an
important part in cost push inflation. Thus, inflation is often transmitted from country to
country. The sharp increase in the world commodity prices, especially oil, in the 1970s
undoubtedly contributed to inflation. Sine inflation is a global phenomenon, it cannot be
avoided. It is not possible for a country to cut itself off completely from rising prices in the
rest of the world.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 173