Page 227 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 227
Macro Economics
Notes
!
Caution Thus, the equations of exchange in its simplest for appears as:
PT = MV
V and T are assumed as constants because at a point of time, given the size and composition
of population, tastes, techniques, resources, purchase habits of the people, etc., the volume
of trade transacted, T and the velocity of circulation of money, V, do not change.
Thus:
P = M, where = some constant, c
P = cM
dP/dM = c
and dP/dM x M/P = 1
This reads that the money elasticity of price level is unitary. That is, a given change in the
quantity of money, M, through any instrument of monetary policy, will induce a same directional
and same proportional change in the general level of prices. An increase in money supply will
raise the price level and it will thus be inflationary whereas a dear money policy will be
deflationary. Monetary policy operates thus because of constancy in V and T. If, for one reason
or the other, the so called constancy assumption does not hold, the entire mechanism of money
policy breaks down.
!
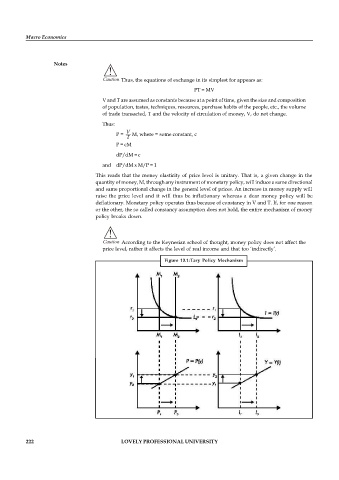
Caution According to the Keynesian school of thought, money policy does not affect the
price level, rather it affects the level of real income and that too ‘indirectly’.
Figure 13.1:Tary Policy Mechanism
222 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY