Page 128 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 128
Unit 7: Variance Analysis
When the actual mix differs from the standard mix: In the second case, standard mix has to Notes
be tuned to the requirement of actual mix, which is revised standard mix, realistic in sense for
meaningful comparison, to highlight the deviation in between two different yields viz. actual
yield and revised standard yield. The standard rate has to be calculated only for the revised
standard mix of materials.
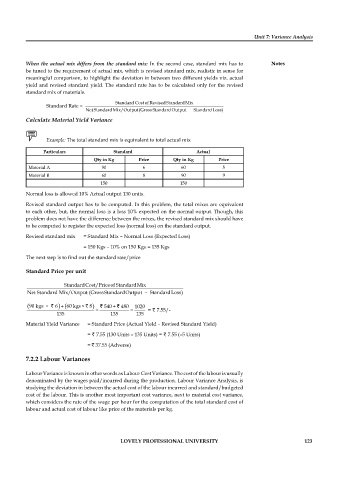
Standard Costof RevisedStandardMix
Standard Rate =
Net StandardMix/Output(GrossStandardOutput – StandardLoss)
Calculate Material Yield Variance
Example: The total standard mix is equivalent to total actual mix
Particulars Standard Actual
Qty in Kg Price Qty in Kg Price
Material A 90 6 60 5
Material B 60 8 90 9
150 150
Normal loss is allowed 10% Actual output 130 units.
Revised standard output has to be computed. In this problem, the total mixes are equivalent
to each other, but, the normal loss is a loss 10% expected on the normal output. Though, this
problem does not have the difference between the mixes, the revised standard mix should have
to be computed to register the expected loss (normal loss) on the standard output.
Revised standard mix = Standard Mix – Normal Loss (Expected Loss)
= 150 Kgs – 10% on 150 Kgs = 135 Kgs
The next step is to find out the standard rate/price
Standard Price per unit
StandardCost/Priceof StandardMix
Net Standard Mix/Output (GrossStandardOutput – StandardLoss)
( × ` )90 kgs 6 + ( × 8 ) 60 kgs = ` 540 + ` 480 = 1020
`
135 135 135 = ` 7.55/-
Material Yield Variance = Standard Price (Actual Yield – Revised Standard Yield)
= ` 7.55 (130 Units – 135 Units) = ` 7.55 (–5 Units)
= ` 37.55 (Adverse)
7.2.2 Labour Variances
Labour Variance is known in other words as Labour Cost Variance. The cost of the labour is usually
denominated by the wages paid/incurred during the production. Labour Variance Analysis, is
studying the deviation in between the actual cost of the labour incurred and standard/budgeted
cost of the labour. This is another most important cost variance, next to material cost variance,
which considers the rate of the wage per hour for the computation of the total standard cost of
labour and actual cost of labour like price of the materials per kg.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 123