Page 206 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 206
Unit 11: Ratio Analysis
Solved Examples Notes
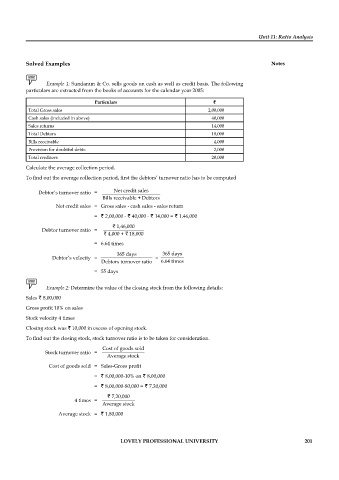
Example 1: Sundaram & Co. sells goods on cash as well as credit basis. The following
particulars are extracted from the books of accounts for the calendar year 2005:
Particulars ` `
Total Gross sales 2,00,000
Cash sales (included in above) 40,000
Sales returns 14,000
Total Debtors 18,000
Bills receivable 4,000
Provision for doubtful debts 2,000
Total creditors 20,000
Calculate the average collection period.
To find out the average collection period, first the debtors’ turnover ratio has to be computed
Debtor’s turnover ratio = Net credit sales
Bills receivable + Debtors
Net credit sales = Gross sales - cash sales - sales return
= ` 2,00,000 - ` 40,000 - ` 14,000 = ` 1,46,000
` 1,46,000
Debtor turnover ratio =
`
` 4,000 + 18,000
= 6.64 times
365 days 365 days
Debtor’s velocity = =
Debtors turnover ratio 6.64 times
= 55 days
Example 2: Determine the value of the closing stock from the following details:
Sales ` 8,00,000
Gross profit 10% on sales
Stock velocity 4 times
Closing stock was ` 10,000 in excess of opening stock.
To find out the closing stock, stock turnover ratio is to be taken for consideration.
Cost of goods sold
Stock turnover ratio =
Average stock
Cost of goods sold = Sales-Gross profi t
= ` 8,00,000-10% on ` 8,00,000
= ` 8,00,000-80,000 = ` 7,20,000
` 7,20,000
4 times =
Average stock
Average stock = ` 1,80,000
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 201