Page 55 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 55
Cost and Management Accounting
Notes Simple Average Method (SAM)
Under the simple average method, the issues are made only on the basis of simple average price.
Defi nition: “Simple Average Price”
“A price which is calculated by dividing the total of the prices of materials in the stock from
which the material to be priced could be drawn by the number of prices used in that total”
The following example will help to understand:
Example: A pillow manufacturer purchases raw cotton from three different quantities at
three different prices.
Quantity Kg ` per Kg
10,000 20
20,000 30
30,000 40
As a manufacturer of pillows, he should find out the cost of the raw cotton material at the moment
of issuance to the production centre. The issue price should be computed as follows:
+ P + P P ...................P
Simple Average Price = 1 2 3 n
N
P = Price of the material purchased at the first instance, P , P and so on.
1 2 3
N = Number of prices involved
20 + ` 30 ` 40
+ `
Simple average price = = ` 30/-
3
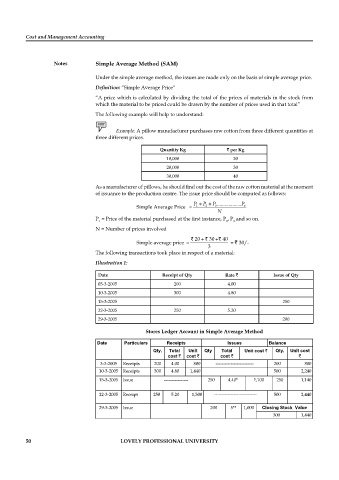
The following transactions took place in respect of a material:
Illustration 1:
Date Receipt of Qty Rate ` Issue of Qty
03-3-2005 200 4.00
10-3-2005 300 4.80
15-3-2005 250
22-3-2005 250 5.20
29-3-2005 200
Stores Ledger Account in Simple Average Method
Date Particulars Receipts Issues Balance
Qty. Total Unit Qty Total Unit cost ` Qty. Unit cost
cost ` cost ` cost ` `
3-3-2005 Receipts 200 4.00 800 ------------------------- 200 800
10-3-2005 Receipts 300 4.80 1,440 500 2,240
15-3-2005 Issue ---------------- 250 4.40* 1,100 250 1,140
22-3-2005 Receipt 250 5.20 1,300 ---------------------------- 500 2,440
29-3-2005 Issue 200 5** 1,000 Closing Stock Value
300 1,440
50 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY