Page 56 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 56
Unit 3: Material Control
The next method is weighted average method to issue the materials from the stores. Why is the Notes
weighted average method considered to be a superior method over the simple average method?
This simple average method does not facilitate the recovery of the cost price of the materials
through the issue price of the material calculated.
From the above cited example, first the cost of the materials is to be computed.
Cost of the materials = (10,000 Kg × ` 20 +20,000 Kg × ` 30 + 30,000 Kg × ` 40)
= ` 2,00,000+ ` 6,00,000 + ` 12,00,000
= ` 20,00,000/-
Recovery through issue under simple average method = 60,000 Kg × ` 30 per Kg = ` 18,00,000
If the issue is made through the simple average method, the cost of materials cannot be recovered
i.e. under recovery
= Cost of the materials- issue price of the material
= ` 20,00,000 – ` 18,00,000 = ` 2,00,000 (Under recovery)
It means that the total issue price is less than that of the cost of the materials by ` 2,00,000.
In order to overcome the above bottleneck which is associated, the method of weighted average
is introduced to replace the early method.
Weighted Average Method (WAM)
Under the weighted average method, the issue price is found out through the appropriate
assignment of weights considered for the determination of weighted average price.
Weighted Average Price
“Weighted average price which is calculated by dividing the total cost of materials in the stock from
which the materials to be priced could be drawn by the total quantity of materials in that stock.”
+ QP + Q P Q P ............Q P
Weighted average price = 11 2 2 3 3 nn
1 + Q 2 + Q Q 3 ......Q n
Q = Quantity of materials
P = Price of the materials
Q = Assigned as weights i.e. volume of the quantities are used weights
The above example is taken for the computation weighted average price
+
+
(10,000 × Kg ` 20 20,000 × Kg ` 30 30,000 × Kg ` 40)
=
+
+ 10,000 20,000 30,000
= ` 33.33 per Kg
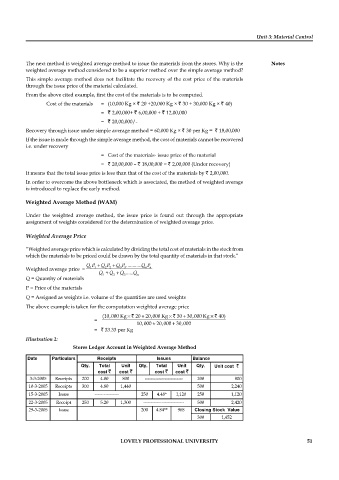
Illustration 2:
Stores Ledger Account in Weighted Average Method
Date Particulars Receipts Issues Balance
Qty. Total Unit Qty. Total Unit Qty. Unit cost `
cost ` cost ` cost ` cost `
3-3-2005 Receipts 200 4.00 800 ------------------------- 200 800
10-3-2005 Receipts 300 4.80 1,440 500 2,240
15-3-2005 Issue ---------------- 250 4.48* 1,120 250 1,120
22-3-2005 Receipt 250 5.20 1,300 --------------------------- 500 2,420
29-3-2005 Issue 200 4.84** 968 Closing Stock Value
300 1,452
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 51