Page 194 - DMGT209_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_II
P. 194
Unit 9: Attitude Measurement and Scaling Techniques
CF = Cumulative frequency for the class just below the median class. Notes
FMd: Frequency of the median class.
i = Size of the class interval of median class.
In the tableN = 300 N/2 = 150. The class containing the 150th person is the median class.
Substitute the value, we get median Md = 21568.
Conclusion: Half of the population has income > 21,568’ and half of the population has income
< 21,568.
Mean
In a grouped data, the midpoint of each category would be multiplied by the number of
observation in that category. Sum up and the total to be divided by the total number of observation.
fx
Eqn., X =
f
Example: Two students X, Y attend 3 class tests and the scores are as follows:
Marks 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test Mean
st
nd
rd
X 55% 60% 65% 60%
Y 65% 60% 55% 60%
Conclusion X - has improved
Y - has deteriorated
Though Mean is the same, X is better than Y.
Measures of Dispersion
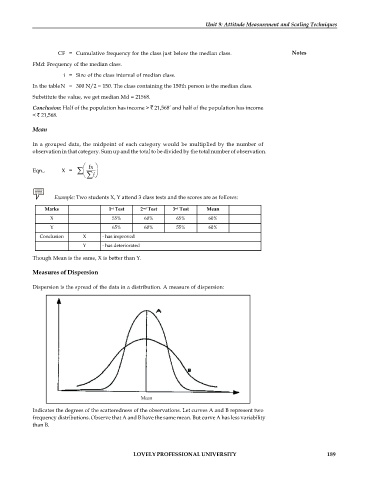
Dispersion is the spread of the data in a distribution. A measure of dispersion:
Indicates the degrees of the scatteredness of the observations. Let curves A and B represent two
frequency distributions. Observe that A and B have the same mean. But curve A has less variability
than B.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 189