Page 156 - DMGT206_PRODUCTION_AND_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 156
Unit 8: Supply Chain Management
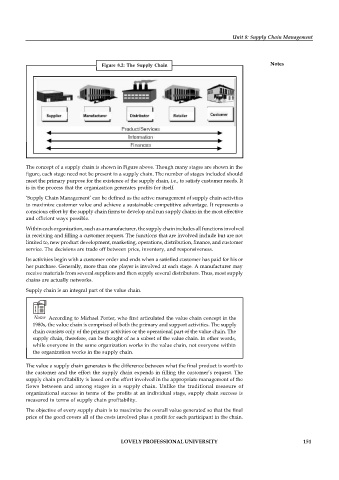
Figure 8.2: The Supply Chain Notes
The concept of a supply chain is shown in Figure above. Though many stages are shown in the
figure, each stage need not be present in a supply chain. The number of stages included should
meet the primary purpose for the existence of the supply chain, i.e., to satisfy customer needs. It
is in the process that the organization generates profits for itself.
‘Supply Chain Management’ can be defined as the active management of supply chain activities
to maximize customer value and achieve a sustainable competitive advantage. It represents a
conscious effort by the supply chain firms to develop and run supply chains in the most effective
and efficient ways possible.
Within each organization, such as a manufacturer, the supply chain includes all functions involved
in receiving and filling a customer request. The functions that are involved include but are not
limited to, new product development, marketing, operations, distribution, finance, and customer
service. The decisions are trade off between price, inventory, and responsiveness.
Its activities begin with a customer order and ends when a satisfied customer has paid for his or
her purchase. Generally, more than one player is involved at each stage. A manufacturer may
receive materials from several suppliers and then supply several distributors. Thus, most supply
chains are actually networks.
Supply chain is an integral part of the value chain.
Notes According to Michael Porter, who first articulated the value chain concept in the
1980s, the value chain is comprised of both the primary and support activities. The supply
chain consists only of the primary activities or the operational part of the value chain. The
supply chain, therefore, can be thought of as a subset of the value chain. In other words,
while everyone in the same organization works in the value chain, not everyone within
the organization works in the supply chain.
The value a supply chain generates is the difference between what the final product is worth to
the customer and the effort the supply chain expends in filling the customer’s request. The
supply chain profitability is based on the effort involved in the appropriate management of the
flows between and among stages in a supply chain. Unlike the traditional measure of
organizational success in terms of the profits at an individual stage, supply chain success is
measured in terms of supply chain profitability.
The objective of every supply chain is to maximize the overall value generated so that the final
price of the good covers all of the costs involved plus a profit for each participant in the chain.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 151