Page 188 - DMGT207_MANAGEMENT_OF_FINANCES
P. 188
Unit 8: Capital Structure Decision
B is the market value of debt Notes
S is the market value of equity
K is the cost of equity
e
The NI approach is based on the following assumptions:
1. The use of debt does not change the risk of investors and therefore, cost of debt (K ) and
d
cost of equity (K ) remains the same irrespective of the degree of leverage.
e
2. Cost of debt is less than the cost of equity.
3. The corporate income tax does not exist.
According to the theory, cost of debt is assumed to be less than the cost of equity. Therefore,
when the financial leverage is increased (proportion of debt in the total capital), the overall cost
of capital will decline and the value of the firm will increase. The implications of the three
assumptions of NI approach is that, as the degree of leverage increases, the proportion of a
cheaper source of funds (debt) in the capital structure increases. As a result, the weighted average
cost of capital tends to decline leading to an increase in the total level of the firm. Thus, even if
the cost of debt and cost of equity remains same regardless of leverage, increased use of low cost
debt will result in the decline of overall cost of capital and thereby, maximize the value of the
firm. So the overall cost of capital will be minimum when the proportion of debt in the capital
structure is maximum. Hence, optimum structure exists when the firm employs 100% debt or
maximum debt in the capital structure.
The NI approach may be compared to a dishonest trader who wants to sell 10 litres of milk
@ 15 per litre. He can add water and pure milk to prepare the 10 litres of milk. If the cost of 1
litre of water is 1, and cost of 1 litre of pure milk is 10, he can maximise his profit or minimize
his cost per litre of milk by adding more and more of low cost water. For example, if he
purchases only pure milk, his cost will be 10×10 = 100. If he adds 5 litres of water to 5 litres
of milk, the cost of 10 litres would be 1×5+10×5 = ( 5.5/litre). Here, pure milk is compared to
equity, which is a costly source, and water is compared to debt, which is a cheaper source.
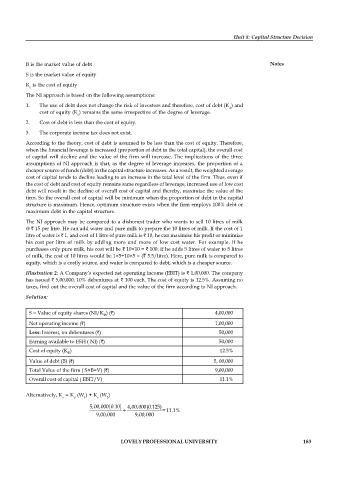
Illustration 2: A Company’s expected net operating income (EBIT) is 1,00,000. The company
has issued 5,00,000, 10% debentures at 100 each. The cost of equity is 12.5%. Assuming no
taxes, find out the overall cost of capital and the value of the firm according to NI approach.
Solution:
S = Value of equity shares (NI/K ) ( ) 4,00,000
e
Net operating income ( ) 1,00,000
Less: Interest, on debentures ( ) 50,000
Earning available to ESH ( NI) ( ) 50,000
Cost of equity (K ) 12.5%
e
Value of debt (B) ( ) 5, 00,000
Total Value of the firm ( S+B=V) ( ) 9,00,000
Overall cost of capital ( EBIT/V) 11.1%
Alternatively, K = K (W ) + K (W )
o d 1 e 2
5,00,000 0.10 4,00,000(0.125)
+ = 11.1%
9,00,000 9,00,000
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 183