Page 193 - DMGT207_MANAGEMENT_OF_FINANCES
P. 193
Management of Finances
Notes hence they would penalize the firm by demanding higher return. Here, advantages of
using low cost debt are less than the disadvantages of higher cost of equity. So the overall
cost of capital increases with leverage and value of the firm decreases.
Thus, the cost of capital decreases with leverage, reaches one minimum point and thereafter,
increases with the leverage.
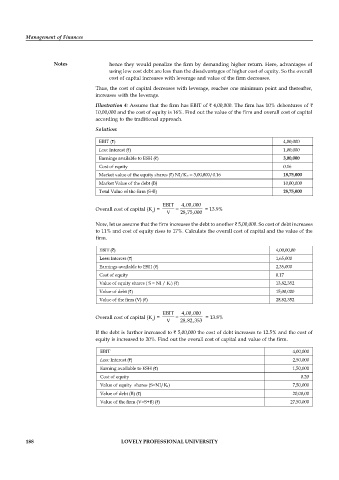
Illustration 4: Assume that the firm has EBIT of 4,00,000. The firm has 10% debentures of
10,00,000 and the cost of equity is 16%. Find out the value of the firm and overall cost of capital
according to the traditional approach.
Solution:
EBIT ( ) 4,00,000
Less: Interest ( ) 1,00,000
Earnings available to ESH ( ) 3,00,000
Cost of equity 0.16
Market value of the equity shares ( ) NI/K e = 3,00,000/0.16 18,75,000
Market Value of the debt (B) 10,00,000
Total Value of the firm (S+B) 28,75,000
EBIT 4,00,000
Overall cost of capital (K ) = = 13.9%
o V 28,75,000
Now, let us assume that the firm increases the debt to another 5,00,000. So cost of debt increases
to 11% and cost of equity rises to 17%. Calculate the overall cost of capital and the value of the
firm.
EBIT ( ) 4,00,00,00
Less: Interest ( ) 1,65,000
Earnings available to ESH ( ) 2,35,000
Cost of equity 0.17
Value of equity shares ( S = NI / K e) ( ) 13,82,352
Value of debt ( ) 15,00,000
Value of the firm (V) ( ) 28,82,352
EBIT 4,00,000
Overall cost of capital (K ) = = 13.8%
o V 28,82,353
If the debt is further increased to 5,00,000 the cost of debt increases to 12.5% and the cost of
equity is increased to 20%. Find out the overall cost of capital and value of the firm.
EBIT 4,00,000
Less: Interest ( ) 2,50,000
Earning available to ESH ( ) 1,50,000
Cost of equity 0.20
Value of equity shares (S=NI/K e) 7,50,000
Value of debt (B) ( ) 20,00,00
Value of the firm (V=S+B) ( ) 27,50,000
188 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY