Page 23 - DMGT303_BANKING_AND_INSURANCE
P. 23
Banking and Insurance
Notes
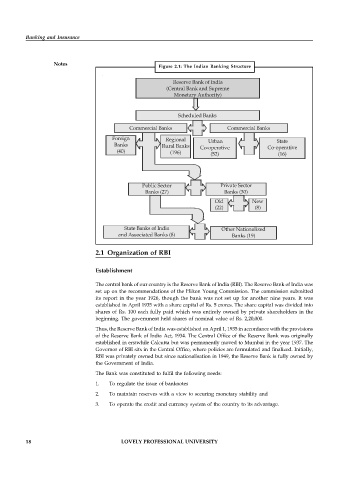
Figure 2.1: The Indian Banking Structure
Reserve Bank of India
(Central Bank and Supreme
Monetary Authority)
Scheduled Banks
Commercial Banks Commercial Banks
Foreign Regional Urban State
Banks Rural Banks Co-operative Co-operative
(40) (196) (52) (16)
Public Sector Private Sector
Banks (27) Banks (30)
Old New
(22) (8)
State Banks of India Other Nationalized
and Associated Banks (8) Banks (19)
2.1 Organization of RBI
Establishment
The central bank of our country is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The Reserve Bank of India was
set up on the recommendations of the Hilton Young Commission. The commission submitted
its report in the year 1926, though the bank was not set up for another nine years. It was
established in April 1935 with a share capital of Rs. 5 crores. The share capital was divided into
shares of Rs. 100 each fully paid which was entirely owned by private shareholders in the
beginning. The government held shares of nominal value of Rs. 2,20,000.
Thus, the Reserve Bank of India was established on April 1, 1935 in accordance with the provisions
of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The Central Office of the Reserve Bank was originally
established in erstwhile Calcutta but was permanently moved to Mumbai in the year 1937. The
Governor of RBI sits in the Central Office, where policies are formulated and finalized. Initially,
RBI was privately owned but since nationalisation in 1949, the Reserve Bank is fully owned by
the Government of India.
The Bank was constituted to fulfil the following needs:
1. To regulate the issue of banknotes
2. To maintain reserves with a view to securing monetary stability and
3. To operate the credit and currency system of the country to its advantage.
18 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY