Page 231 - DMGT303_BANKING_AND_INSURANCE
P. 231
Banking and Insurance
Notes
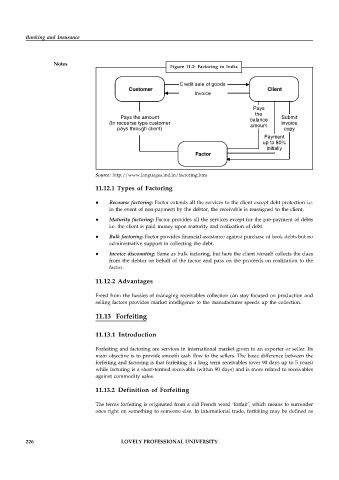
Figure 11.2: Factoring in India
Credit sale of goods
Customer Client
Invoice
Pays
the
Pays the amount balance Submit
(In recourse type customer amount invoice
pays through client) copy
Payment
up to 80%
initially
Factor
Source: http://www.languages.ind.in/factoring.htm
11.12.1 Types of Factoring
Recourse factoring: Factor extends all the services to the client except debt protection i.e.
in the event of non-payment by the debtor, the receivable is reassigned to the client.
Maturity factoring: Factor provides all the services except for the pre-payment of debts
i.e. the client is paid money upon maturity and realization of debt.
Bulk factoring: Factor provides financial assistance against purchase of book debts but no
administrative support in collecting the debt.
Invoice discounting: Same as bulk factoring, but here the client himself collects the dues
from the debtor on behalf of the factor and pass on the proceeds on realization to the
factor.
11.12.2 Advantages
Freed from the hassles of managing receivables collection can stay focused on production and
selling factors provides market intelligence to the manufacturer speeds up the collection.
11.13 Forfeiting
11.13.1 Introduction
Forfeiting and factoring are services in international market given to an exporter or seller. Its
main objective is to provide smooth cash flow to the sellers. The basic difference between the
forfeiting and factoring is that forfeiting is a long term receivables (over 90 days up to 5 years)
while factoring is a short-termed receivable (within 90 days) and is more related to receivables
against commodity sales.
11.13.2 Definition of Forfeiting
The terms forfeiting is originated from a old French word ‘forfait’, which means to surrender
ones right on something to someone else. In international trade, forfeiting may be defined as
226 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY