Page 195 - DMGT402_MANAGEMENT_PRACTICES_AND_ORGANIZATIONAL_BEHAVIOUR
P. 195
Management Practices and Organisational Behaviour
Notes For example working hard and getting the promotion will probably cause the person to keep
working hard in the future.
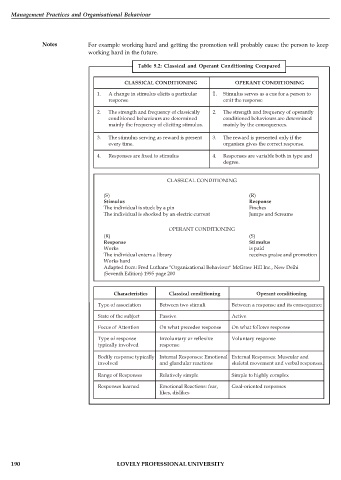
Table 9.2: Classical and Operant Conditioning Compared
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING OPERANT CONDITIONING
1. A change in stimulus elicits a particular 1. Stimulus serves as a cue for a person to
response emit the response
2. The strength and frequency of classically 2. The strength and frequency of operantly
conditioned behaviours are determined conditioned behaviours are determined
mainly the frequency of eliciting stimulus. mainly by the consequences.
3. The stimulus serving as reward is present 3. The reward is presented only if the
every time. organism gives the correct response.
4. Responses are fixed to stimulus 4. Responses are variable both in type and
degree.
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
(S) (R)
Stimulus Response
The individual is stuck by a pin Finches
The individual is shocked by an electric current Jumps and Screams
OPERANT CONDITIONING
(R) (S)
Response Stimulus
Works is paid
The individual enters a library receives praise and promotion
Works hard
Adapted from: Fred Luthans "Organizational Behaviour" McGraw Hill Inc., New Delhi
(Seventh Edition) 1995 page 200
Characteristics Classical conditioning Operant conditioning
Type of association Between two stimuli Between a response and its consequence
State of the subject Passive Active
Focus of Attention On what precedes response On what follows response
Type of response Involuntary or reflexive Voluntary response
typically involved response
Bodily response typically Internal Responses: Emotional External Responses: Muscular and
involved and glandular reactions skeletal movement and verbal responses.
Range of Responses Relatively simple Simple to highly complex
Responses learned Emotional Reactions: fear, Goal-oriented responses
likes, dislikes
190 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY