Page 121 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 121
Accounting for Managers
Notes The accounting ratios are applied to study the relationship in between the quantitative
information available and to take decision on the financial performance of the firm.
According to J. Betty, “The term accounting is used to describe relationships significantly which
exist in between figures shown in a balance sheet, Profit & Loss A/c, Trading A/c, Budgetary
control system or in any part of the accounting organization.”
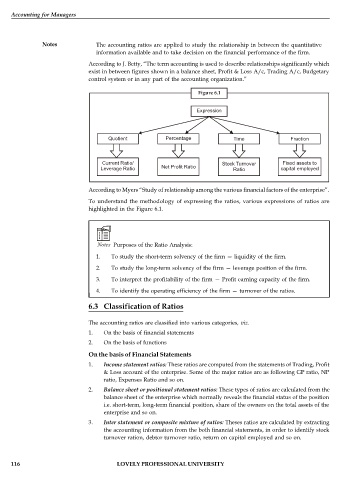
Figure 6.1
Expression
Quotient Percentage Time Fraction
Current Ratio/ Stock Turnover Fixed assets to
Leverage Ratio Net Profit Ratio Ratio capital employed
According to Myers “Study of relationship among the various financial factors of the enterprise”.
To understand the methodology of expressing the ratios, various expressions of ratios are
highlighted in the Figure 6.1.
Notes Purposes of the Ratio Analysis:
1. To study the short-term solvency of the firm — liquidity of the firm.
2. To study the long-term solvency of the firm — leverage position of the firm.
3. To interpret the profitability of the firm — Profit earning capacity of the firm.
4. To identify the operating efficiency of the firm — turnover of the ratios.
6.3 Classification of Ratios
The accounting ratios are classified into various categories, viz.
1. On the basis of financial statements
2. On the basis of functions
On the basis of Financial Statements
1. Income statement ratios: These ratios are computed from the statements of Trading, Profit
& Loss account of the enterprise. Some of the major ratios are as following GP ratio, NP
ratio, Expenses Ratio and so on.
2. Balance sheet or positional statement ratios: These types of ratios are calculated from the
balance sheet of the enterprise which normally reveals the financial status of the position
i.e. short-term, long-term financial position, share of the owners on the total assets of the
enterprise and so on.
3. Inter statement or composite mixture of ratios: Theses ratios are calculated by extracting
the accounting information from the both financial statements, in order to identify stock
turnover ration, debtor turnover ratio, return on capital employed and so on.
116 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY