Page 124 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 124
Unit 6: Financial Statements: Analysis and Interpretation
Notes
Example: A company has a closing stock of 30,000 while its prepaid expenses are
5000. What will be its quick assets ratio if the current assets are worth 50000 while current
liabilities are worth 15000?
Solution:
Liquid Asset = Current Assets – (Closing Stock + Prepaid Expenses)
= 50000 – (30000 + 5000)
= 15000
Liquid Assets
Quick Assets Ratio =
Current Liabilities
= 15000/15000 = 1:1
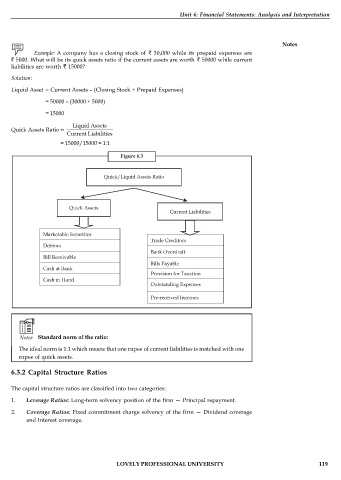
Figure 6.3
Notes Standard norm of the ratio:
The ideal norm is 1:1 which means that one rupee of current liabilities is matched with one
rupee of quick assets.
6.3.2 Capital Structure Ratios
The capital structure ratios are classified into two categories:
1. Leverage Ratios: Long-term solvency position of the firm — Principal repayment.
2. Coverage Ratios: Fixed commitment charge solvency of the firm — Dividend coverage
and Interest coverage.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 119