Page 240 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 240
Unit 11: Variance Analysis
Solution: Notes
First step is to compute the labour cost variance
= (Standard Hrs for Actual Output × Standard Rate) – (Actual Hours × Actual Rate)
= (2,000 Hrs × 2) – (1,900 Hrs × 2.50)
= 4,000 – 4,750
= 750 (Adverse)
The next step is to find out the labour rate variance
= Actual Hours (Standard Rate – Actual Rate)
= 1,900 Hours (2 – 2.50) = 950 (Adverse)
The next variance is to be found out the labour efficiency variance
= Standard Rate (Standard Hours for Actual Output – Acutal Hours)
= 2.00 (2,000 – 1,900) = 200 (Favourable)
Verification
Labour Cost Variance = Labour Rate Variance + Labour Efficiency Variance
750 (Adverse) = 950 (Adverse) + 200 (Favourable)
750 (Adverse) = 750 (Adverse)
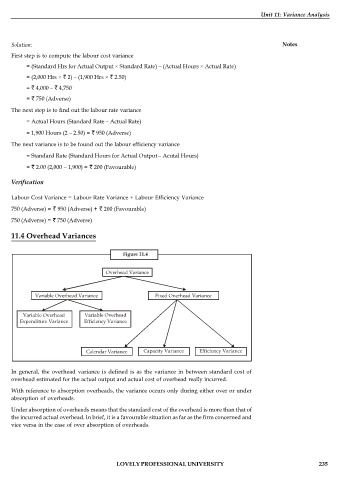
11.4 Overhead Variances
Figure 11.4
Overhead Variance
Variable Overhead Variance Fixed Overhead Variance
Variable Overhead Variable Overhead
Expenditure Variance Efficiency Variance
Calendar Variance Capacity Variance Efficiency Variance
In general, the overhead variance is defined is as the variance in between standard cost of
overhead estimated for the actual output and actual cost of overhead really incurred.
With reference to absorption overheads, the variance occurs only during either over or under
absorption of overheads.
Under absorption of overheads means that the standard cost of the overhead is more than that of
the incurred actual overhead. In brief, it is a favourable situation as far as the firm concerned and
vice versa in the case of over absorption of overheads.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 235