Page 259 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 259
Accounting for Managers
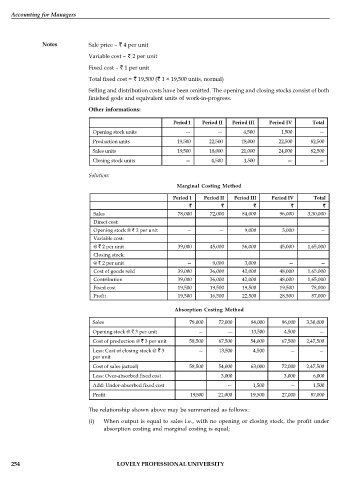
Notes Sale price – 4 per unit
Variable cost – 2 per unit
Fixed cost – 1 per unit
Total fixed cost = 19,500 ( 1 × 19,500 units, normal)
Selling and distribution costs have been omitted. The opening and closing stocks consist of both
finished gods and equivalent units of work-in-progress.
Other informations:
Period 1 Period II Period III Period IV Total
Opening stock units — — 4,500 1,500 —
Production units 19,500 22,500 18,000 22,500 82,500
Sales units 19,500 18,000 21,000 24,000 82,500
Closing stock units — 4,500 1,500 — —
Solution:
Marginal Costing Method
Period 1 Period II Period III Period IV Total
Sales 78,000 72,000 84,000 96,000 3,30,000
Direct cost:
Opening stock @ 2 per unit — — 9,000 3,000 —
Variable cost:
@ 2 per unit 39,000 45,000 36,000 45,000 1,65,000
Closing stock:
@ 2 per unit — 9,000 3,000 — —
Cost of goods sold 39,000 36,000 42,000 48,000 1,65,000
Contribution 39,000 36,000 42,000 48,000 1,65,000
Fixed cost 19,500 19,500 19,500 19,500 78,000
Profit 19,500 16,500 22,500 28,500 87,000
Absorption Costing Method
Sales 78,000 72,000 84,000 96,000 3,30,000
Opening stock @ 3 per unit — -— 13,500 4,500 —
Cost of production @ 3 per unit 58,500 67,500 54,000 67,500 2,47,500
Less: Cost of closing stock @ 3 — 13,500 4,500 — —
per unit
Cost of sales (actual) 58,500 54,000 63,000 72,000 2,47,500
Less: Over-absorbed fixed cost 3,000 3,000 6,000
Add: Under-absorbed fixed cost — 1,500 — 1,500
Profit 19,500 21,000 19,500 27,000 87,000
The relationship shown above may be summarized as follows:
(i) When output is equal to sales i.e., with no opening or closing stock, the profit under
absorption costing and marginal costing is equal;
254 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY