Page 163 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 163
Unit 8: Descriptive Statistics
Empirical Relation between Mean, Median and Mode Notes
Empirically, it has been observed that for a moderately skewed distribution, the difference
between mean and mode is approximately three times the difference between mean and median,
i.e., X M o 3 X M d .
This relation can be used to estimate the value of one of the measures when the values of the
other two are known.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
3. ................................ is defined as the sum of observations divided by the number of
observations.
4. ................................ is used when the magnitude of individual observations is large.
5. Median and mode are also known as the ................................ averages.
6. In a grouped frequency distribution, there are classes along with their respective
................................
7. ................................ check of accuracy is used when the arithmetic mean of a frequency
distribution is calculated by shortcut or step-deviation method.
8. Median of distribution is that value of the variate which divides it into ................................
parts.
9. The total area under a histogram is equal to total ................................
10. ................................ divide a distribution into 10 equal parts.
11. A distribution may have only ................................ quartiles.
12. Mode is that value of the variate which occurs ................................ number of times in a
distribution.
13. It is ................................ around which other items are most densely distributed.
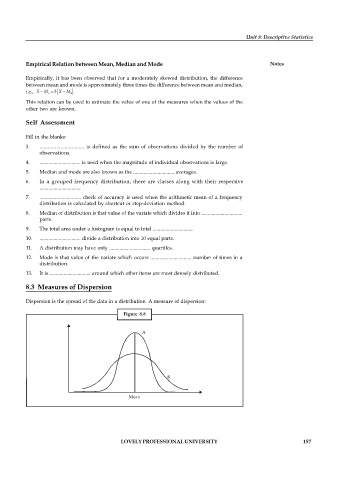
8.3 Measures of Dispersion
Dispersion is the spread of the data in a distribution. A measure of dispersion:
Figure 8.8
A
B
Mean
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 157