Page 229 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 229
Unit 10: Time Series
Merits and Demerits Notes
It is an objective method of measuring seasonal variations. However, it is very complicated and
doesn't work if cyclical variations are present.
10.6.3 Ratio to Moving Average Method
The ratio to moving average is the most commonly used method of measuring seasonal
variations. This method assumes the presence of all the four components of a time series.
Various steps in the computation of seasonal indices are as follows:
1. Compute the moving averages with period equal to the period of seasonal variations.
This would eliminate the seasonal component and minimise the effect of random
component. The resulting moving averages would consist of trend, cyclical and random
components.
2. The original values, for each quarter (or month) are divided by the respective moving
Y TCSR
average figures and the ratio is expressed as a percentage, i.e., = SR’’, where
M .A TCR
R’ and R’’ denote the changed random components.
3. Finally, the random component R’’ is eliminated by the method of simple averages.
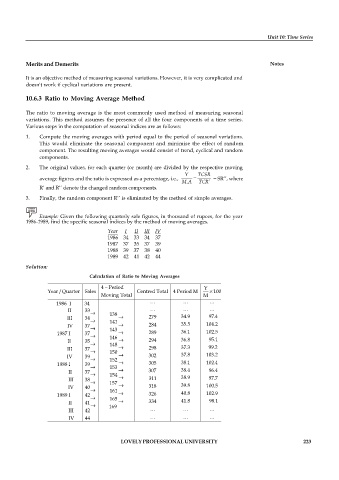
Example: Given the following quarterly sale figures, in thousand of rupees, for the year
1986-1989, find the specific seasonal indices by the method of moving averages.
Year I II III IV
1986 34 33 34 37
1987 37 35 37 39
1988 39 37 38 40
1989 42 41 42 44
Solution:
Calculation of Ratio to Moving Averages
-
4 Period Y
Year/Quarter Sales Centred Total 4 Period M 100
Moving Total M
1986 I 34
II 33
® 138
III 34 ® ® 279 34.9 97.4
IV 37 141 ® 284 35.5 104.2
® 143
1987 I 37 ® ® 289 36.1 102.5
II 35 146 ® 294 36.8 95.1
® 148
III 37 ® 150 ® 298 37.3 99.2
IV 39 ® 302 37.8 103.2
® 152
1988 I 39 ® 153 ® 305 38.1 102.4
II 37 ® 307 38.4 96.4
® 154 ®
III 38 ® 157 311 38.9 97.7
IV 40 ® 318 39.8 100.5
® 161 ®
1989 I 42 ® 326 40.8 102.9
II 41 165 ® 334 41.8 98.1
® 169
III 42
IV 44
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 223