Page 242 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 242
Research Methodology
Notes 1
1 n n log P i
P = P × P ×..... P ) n = P i = Antilog
n
01
2
1
i=1 n
( is used to denote the product of terms.)
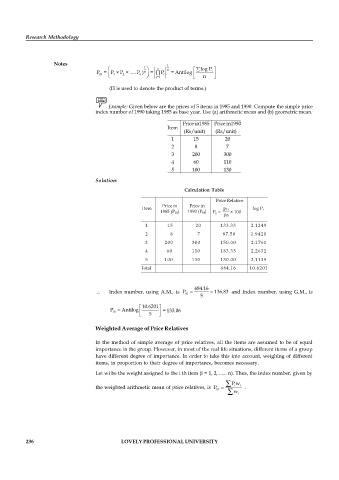
Example: Given below are the prices of 5 items in 1985 and 1990. Compute the simple price
index number of 1990 taking 1985 as base year. Use (a) arithmetic mean and (b) geometric mean.
Price in1985 Price in1990
Item
(Rs/unit) (Rs/unit)
1 15 20
2 8 7
3 200 300
4 60 110
5 100 130
Solution:
Calculation Table
Price Relative
Price in Price in
Item p log P i
1i
1985 (P ) 1990 (P ) P i = × 100
0i
0i
p 0i
1 15 20 133.33 2.1249
2 8 7 87.50 1.9420
3 200 300 150.00 2.1761
4 60 110 183.33 2.2632
5 100 130 130.00 2.1139
Total 684.16 10.6201
\ Index number, using A.M., is P = 684.16 = 136.83 and Index number, using G.M., is
01
5
é 10.6201ù
P = Antilog
01 ê ë 5 ú û = 133.06
Weighted Average of Price Relatives
In the method of simple average of price relatives, all the items are assumed to be of equal
importance in the group. However, in most of the real life situations, different items of a group
have different degree of importance. In order to take this into account, weighing of different
items, in proportion to their degree of importance, becomes necessary.
Let wi be the weight assigned to the i th item (i = 1, 2, ...... n). Thus, the index number, given by
å P w
the weighted arithmetic mean of price relatives, is P = i i .
01 å w i
236 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY