Page 247 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 247
Unit 11: Index Numbers
Solution: Notes
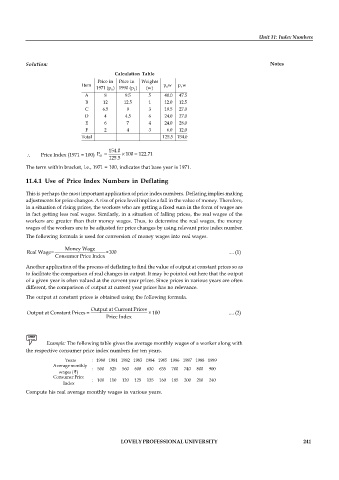
Calculation Table
Price in Price in Weights
Item p w p w
1971 (p ) 1990 (p ) (w) 0 1
1
0
A 8 9.5 5 40.0 47.5
B 12 12.5 1 12.0 12.5
C 6.5 9 3 19.5 27.0
D 4 4.5 6 24.0 27.0
E 6 7 4 24.0 28.0
F 2 4 3 6.0 12.0
Total 125.5 154.0
154.0
\ Price Index (1971 = 100) P = ´ 100 = 122.71
01
125.5
The term within bracket, i.e., 1971 = 100, indicates that base year is 1971.
11.4.1 Use of Price Index Numbers in Deflating
This is perhaps the most important application of price index numbers. Deflating implies making
adjustments for price changes. A rise of price level implies a fall in the value of money. Therefore,
in a situation of rising prices, the workers who are getting a fixed sum in the form of wages are
in fact getting less real wages. Similarly, in a situation of falling prices, the real wages of the
workers are greater than their money wages. Thus, to determine the real wages, the money
wages of the workers are to be adjusted for price changes by using relevant price index number.
The following formula is used for conversion of money wages into real wages.
Money Wage
Real Wage= ×100 .... (1)
Consumer Price Index
Another application of the process of deflating to find the value of output at constant prices so as
to facilitate the comparison of real changes in output. It may be pointed out here that the output
of a given year is often valued at the current year prices. Since prices in various years are often
different, the comparison of output at current year prices has no relevance.
The output at constant prices is obtained using the following formula.
Output at Current Prices
Output at Constant Prices = × 100 .... (2)
Price Index
Example: The following table gives the average monthly wages of a worker along with
the respective consumer price index numbers for ten years.
Y e a r s : 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989
Average monthly
: 500 525 560 600 630 635 700 740 800 900
wages( )
Consumer Price
: 100 110 120 125 135 160 185 200 210 240
I ndex
Compute his real average monthly wages in various years.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 241