Page 249 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 249
Unit 11: Index Numbers
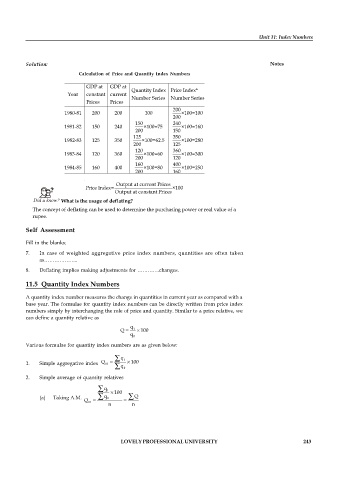
Solution: Notes
Calculation of Price and Quantity Index Numbers
GDP at GDP at
Quantity Index Price Index*
Year constant current
Number Series Number Series
Prices Prices
200
1980-81 200 200 100 ×100=100
200
150 240
1981-82 150 240 ×100=75 ×100=160
200 150
125 350
1982-83 125 350 ×100=62.5 ×100=280
200 125
120 360
1983-84 120 360 ×100=60 ×100=300
200 120
160 400
1984-85 160 400 ×100=80 ×100=250
200 160
Output at current Prices
Price Index= ×100
Output at constant Prices
Did u know? What is the usage of deflating?
The concept of deflating can be used to determine the purchasing power or real value of a
rupee.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
7. In case of weighted aggregative price index numbers, quantities are often taken
as………………..
8. Deflating implies making adjustments for ………….changes.
11.5 Quantity Index Numbers
A quantity index number measures the change in quantities in current year as compared with a
base year. The formulae for quantity index numbers can be directly written from price index
numbers simply by interchanging the role of price and quantity. Similar to a price relative, we
can define a quantity relative as
Q = q 1 ´ 100
q 0
Various formulae for quantity index numbers are as given below:
å q
Q = 1 ´ 100
1. Simple aggregative index 01 å q 0
2. Simple average of quantity relatives
å q 1 ´
(a) Taking A.M. å q 0 100 å Q
Q = =
01
n n
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 243