Page 269 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 269
Unit 12: Hypothesis Testing
We note that the mean will exist if v > 2 and standard error will exist if v > 4. Further, the Notes
2 2
mean > 1.
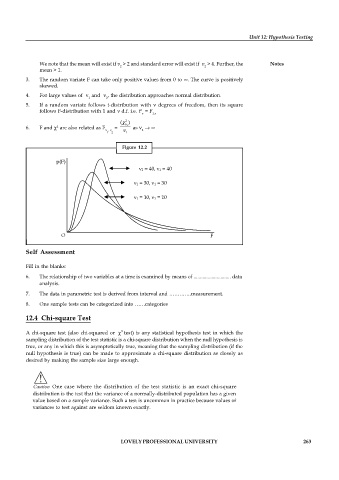
3. The random variate F can take only positive values from 0 to . The curve is positively
skewed.
4. For large values of and , the distribution approaches normal distribution.
1 2
5. If a random variate follows t-distribution with degrees of freedom, then its square
2
follows F-distribution with 1 and d.f. i.e. t = F 1,
( 2 )
6. F and are also related as F = 1 v as
2
, 2
1 2 1
Figure 12.2
p(F)
1 = 40, 1 = 40
1 = 30, 1 = 30
1 = 10, 1 = 10
O F
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
6. The relationship of two variables at a time is examined by means of ............................. data
analysis.
7. The data in parametric test is derived from interval and ………….measurement.
8. One sample tests can be categorized into ……categories
12.4 Chi-square Test
2
A chi-square test (also chi-squared or test) is any statistical hypothesis test in which the
sampling distribution of the test statistic is a chi-square distribution when the null hypothesis is
true, or any in which this is asymptotically true, meaning that the sampling distribution (if the
null hypothesis is true) can be made to approximate a chi-square distribution as closely as
desired by making the sample size large enough.
!
Caution One case where the distribution of the test statistic is an exact chi-square
distribution is the test that the variance of a normally-distributed population has a given
value based on a sample variance. Such a test is uncommon in practice because values of
variances to test against are seldom known exactly.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 263