Page 191 - DMGT408DMGT203_Marketing Management
P. 191
Marketing Management/Essentials of Marketing
Notes
Example: Product pricing may depend heavily on the productivity of a manufacturing
facility (e.g., how much can be produced within a certain period of time). The marketer knows
that increasing productivity can reduce the cost of producing each product and thus allow the
marketer to potentially lower the product’s price. But increasing productivity may require
major changes at the manufacturing facility that will take time (not to mention be costly) and
will not translate into lower price products for a considerable period of time.
2. External Factors: There are a number of influencing factors which are not controlled by
the company but will impact pricing decisions. Understanding these factors requires the
marketer conduct research to monitor what is happening in each market the company
serves since the effect of these factors can vary by market.
Task List all the internal and external factors that affect the pricing of:
1. Necessary goods
2. Luxury goods
3. Unsought goods, like insurance
Competitive Structure: The market conditions vary considerably and market structure affects
not only the pricing decisions within a company but also the kind of likely response from other
players in the same industry. Much depends on the number of buyers and sellers operating in a
market and the extent of entry and exit barriers. These factors affect a company’s level of flexibility
in setting prices.
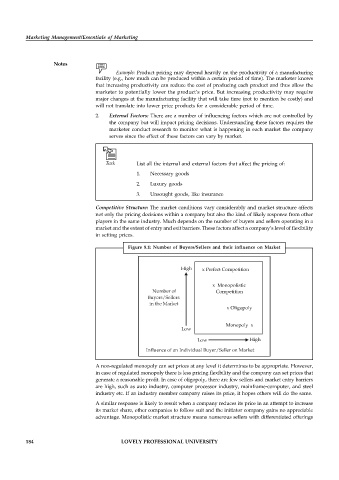
Figure 8.1: Number of Buyers/Sellers and their influence on Market
High x Perfect Competition
x Monopolistic
Number of Competition
Buyers/Sellers
in the Market
x Oligopoly
Monopoly x
Low
Low High
Influence of an Individual Buyer/Seller on Market
A non-regulated monopoly can set prices at any level it determines to be appropriate. However,
in case of regulated monopoly there is less pricing flexibility and the company can set prices that
generate a reasonable profit. In case of oligopoly, there are few sellers and market entry barriers
are high, such as auto industry, computer processor industry, mainframe-computer, and steel
industry etc. If an industry member company raises its price, it hopes others will do the same.
A similar response is likely to result when a company reduces its price in an attempt to increase
its market share, other companies to follow suit and the initiator company gains no appreciable
advantage. Monopolistic market structure means numerous sellers with differentiated offerings
184 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY