Page 285 - DMGT408DMGT203_Marketing Management
P. 285
Marketing Management/Essentials of Marketing
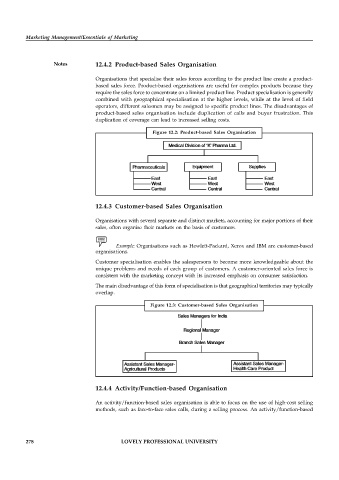
Notes 12.4.2 Product-based Sales Organisation
Organisations that specialise their sales forces according to the product line create a product-
based sales force. Product-based organisations are useful for complex products because they
require the sales force to concentrate on a limited product line. Product specialisation is generally
combined with geographical specialisation at the higher levels, while at the level of field
operators, different salesmen may be assigned to specific product lines. The disadvantages of
product-based sales organisation include duplication of calls and buyer frustration. This
duplication of coverage can lead to increased selling costs.
Figure 12.2: Product-based Sales Organisation
12.4.3 Customer-based Sales Organisation
Organisations with several separate and distinct markets, accounting for major portions of their
sales, often organise their markets on the basis of customers.
Example: Organisations such as Hewlett-Packard, Xerox and IBM are customer-based
organisations.
Customer specialisation enables the salespersons to become more knowledgeable about the
unique problems and needs of each group of customers. A customer-oriented sales force is
consistent with the marketing concept with its increased emphasis on consumer satisfaction.
The main disadvantage of this form of specialisation is that geographical territories may typically
overlap.
Figure 12.3: Customer-based Sales Organisation
12.4.4 Activity/Function-based Organisation
An activity/function-based sales organisation is able to focus on the use of high-cost selling
methods, such as face-to-face sales calls, during a selling process. An activity/function-based
278 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY