Page 151 - DCOM506_DMGT502_STRATEGIC_MANAGEMENT
P. 151
Unit 8: Business Level Strategies
4. Innovative marketing capabilities Notes
5. Motivation for innovation
6. Corporate reputation for quality or technological capabilities.
How Differentiation Delivers Above-average Profits?
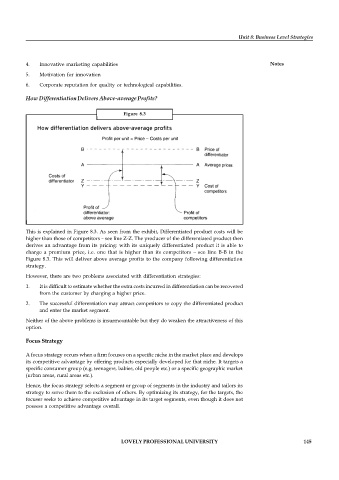
Figure 8.3
This is explained in Figure 8.3. As seen from the exhibit, Differentiated product costs will be
higher than those of competitors – see line Z-Z. The producer of the differentiated product then
derives an advantage from its pricing: with its uniquely differentiated product it is able to
charge a premium price, i.e. one that is higher than its competitors – see line B-B in the
Figure 8.3. This will deliver above average profits to the company following differentiation
strategy.
However, there are two problems associated with differentiation strategies:
1. It is difficult to estimate whether the extra costs incurred in differentiation can be recovered
from the customer by charging a higher price.
2. The successful differentiation may attract competitors to copy the differentiated product
and enter the market segment.
Neither of the above problems is insurmountable but they do weaken the attractiveness of this
option.
Focus Strategy
A focus strategy occurs when a firm focuses on a specific niche in the market place and develops
its competitive advantage by offering products especially developed for that niche. It targets a
specific consumer group (e.g. teenagers, babies, old people etc.) or a specific geographic market
(urban areas, rural areas etc.).
Hence, the focus strategy selects a segment or group of segments in the industry and tailors its
strategy to serve them to the exclusion of others. By optimizing its strategy, for the targets, the
focuser seeks to achieve competitive advantage in its target segments, even though it does not
possess a competitive advantage overall.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 145