Page 151 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 151
Unit 5: Facility Location
Notes
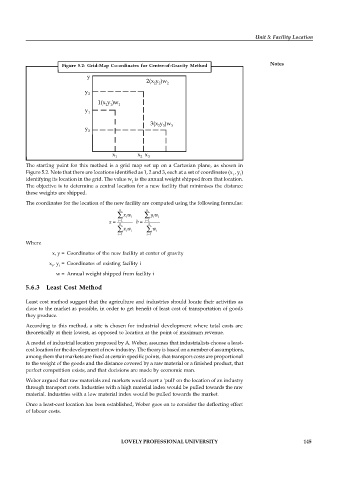
Figure 5.2: Grid-Map Co-ordinates for Centre-of-Gravity Method
y
2(x y )w
2 2 2
y
2
1(x y )w 1
1 1
y
1
3(x y )w 3
3 3
y 3
x x x
1 2 3
The starting point for this method is a grid map set up on a Cartesian plane, as shown in
Figure 5.2. Note that there are locations identified as 1, 2 and 3, each at a set of coordinates (x , y )
1 1
identifying its location in the grid. The value w is the annual weight shipped from that location.
1
The objective is to determine a central location for a new facility that minimises the distance
these weights are shipped.
The coordinates for the location of the new facility are computed using the following formulas:
n n
x w i y w i
i
i
x i 1 b i 1
n n
x w i w i
i
i 1 i 1
Where
x, y = Coordinates of the new facility at center of gravity
x , y = Coordinates of existing facility i
1 1
w = Annual weight shipped from facility i
5.6.3 Least Cost Method
Least cost method suggest that the agriculture and industries should locate their activities as
close to the market as possible, in order to get benefit of least cost of transportation of goods
they produce.
According to this method, a site is chosen for industrial development where total costs are
theoretically at their lowest, as opposed to location at the point of maximum revenue.
A model of industrial location proposed by A. Weber, assumes that industrialists choose a least-
cost location for the development of new industry. The theory is based on a number of assumptions,
among them that markets are fixed at certain specific points, that transport costs are proportional
to the weight of the goods and the distance covered by a raw material or a finished product, that
perfect competition exists, and that decisions are made by economic man.
Weber argued that raw materials and markets would exert a 'pull' on the location of an industry
through transport costs. Industries with a high material index would be pulled towards the raw
material. Industries with a low material index would be pulled towards the market.
Once a least-cost location has been established, Weber goes on to consider the deflecting effect
of labour costs.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 145