Page 97 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 97
Unit 4: Process Selection and Facility Layout
process and the two stages are directly linked. In a continuous process, the most common Notes
problems are 'blocking' and 'starving'.
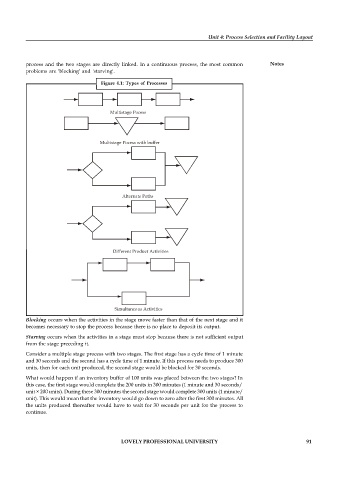
Figure 4.1: Types of Processes
Multistage Pocess
Multistage Pocess with buffer
Alternate Paths
Different Product Activities
Simultaneous Activities
Blocking occurs when the activities in the stage move faster than that of the next stage and it
becomes necessary to stop the process because there is no place to deposit its output.
Starving occurs when the activities in a stage must stop because there is not sufficient output
from the stage preceding it.
Consider a multiple stage process with two stages. The first stage has a cycle time of 1 minute
and 30 seconds and the second has a cycle time of 1 minute. If this process needs to produce 300
units, then for each unit produced, the second stage would be blocked for 30 seconds.
What would happen if an inventory buffer of 100 units was placed between the two stages? In
this case, the first stage would complete the 200 units in 300 minutes (1 minute and 30 seconds/
unit × 200 units). During these 300 minutes the second stage would complete 300 units (1 minute/
unit). This would mean that the inventory would go down to zero after the first 300 minutes. All
the units produced thereafter would have to wait for 30 seconds per unit for the process to
continue.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 91