Page 128 - DMGT506_CONSUMER_BEHAVIOUR
P. 128
Unit 9: Reference Group Influences
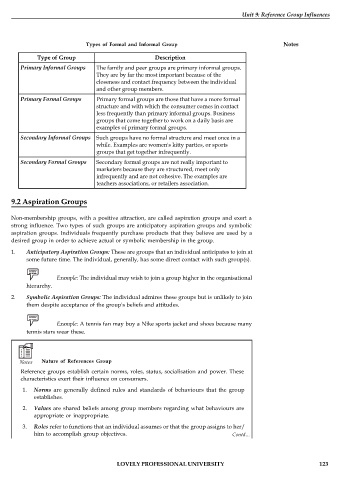
Types of Formal and Informal Group Notes
Type of Group Description
Primary Informal Groups The family and peer groups are primary informal groups.
They are by far the most important because of the
closeness and contact frequency between the individual
and other group members.
Primary Formal Groups Primary formal groups are those that have a more formal
structure and with which the consumer comes in contact
less frequently than primary informal groups. Business
groups that come together to work on a daily basis are
examples of primary formal groups.
Secondary Informal Groups Such groups have no formal structure and meet once in a
while. Examples are women's kitty parties, or sports
groups that get together infrequently.
Secondary Formal Groups Secondary formal groups are not really important to
marketers because they are structured, meet only
infrequently and are not cohesive. The examples are
teachers associations, or retailers association.
9.2 Aspiration Groups
Non-membership groups, with a positive attraction, are called aspiration groups and exert a
strong influence. Two types of such groups are anticipatory aspiration groups and symbolic
aspiration groups. Individuals frequently purchase products that they believe are used by a
desired group in order to achieve actual or symbolic membership in the group.
1. Anticipatory Aspiration Groups: These are groups that an individual anticipates to join at
some future time. The individual, generally, has some direct contact with such group(s).
Example: The individual may wish to join a group higher in the organisational
hierarchy.
2. Symbolic Aspiration Groups: The individual admires these groups but is unlikely to join
them despite acceptance of the group's beliefs and attitudes.
Example: A tennis fan may buy a Nike sports jacket and shoes because many
tennis stars wear these.
Notes Nature of References Group
Reference groups establish certain norms, roles, status, socialisation and power. These
characteristics exert their influence on consumers.
1. Norms are generally defined rules and standards of behaviours that the group
establishes.
2. Values are shared beliefs among group members regarding what behaviours are
appropriate or inappropriate.
3. Roles refer to functions that an individual assumes or that the group assigns to her/
him to accomplish group objectives. Contd...
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 123