Page 198 - DMGT506_CONSUMER_BEHAVIOUR
P. 198
Unit 14: Opinion Leadership and Diffusion of Innovation
Notes
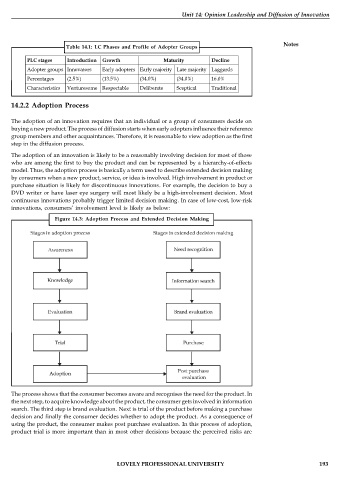
Table 14.1: LC Phases and Profile of Adopter Groups
PLC stages Introduction Growth Maturity Decline
Adopter groups Innovators Early adopters Early majority Late majority Laggards
Percentages (2.5%) (13.5%) (34.0%) (34.0%) 16.0%
Characteristics Venturesome Respectable Deliberate Sceptical Traditional
14.2.2 Adoption Process
The adoption of an innovation requires that an individual or a group of consumers decide on
buying a new product. The process of diffusion starts when early adopters influence their reference
group members and other acquaintances. Therefore, it is reasonable to view adoption as the first
step in the diffusion process.
The adoption of an innovation is likely to be a reasonably involving decision for most of those
who are among the first to buy the product and can be represented by a hierarchy-of-effects
model. Thus, the adoption process is basically a term used to describe extended decision making
by consumers when a new product, service, or idea is involved. High involvement in product or
purchase situation is likely for discontinuous innovations. For example, the decision to buy a
DVD writer or have laser eye surgery will most likely be a high-involvement decision. Most
continuous innovations probably trigger limited decision making. In case of low-cost, low-risk
innovations, consumers’ involvement level is likely as below:
Figure 14.3: Adoption Process and Extended Decision Making
The process shows that the consumer becomes aware and recognises the need for the product. In
the next step, to acquire knowledge about the product, the consumer gets involved in information
search. The third step is brand evaluation. Next is trial of the product before making a purchase
decision and finally the consumer decides whether to adopt the product. As a consequence of
using the product, the consumer makes post purchase evaluation. In this process of adoption,
product trial is more important than in most other decisions because the perceived risks are
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 193