Page 22 - DMGT506_CONSUMER_BEHAVIOUR
P. 22
Unit 2: Consumer Research
Notes
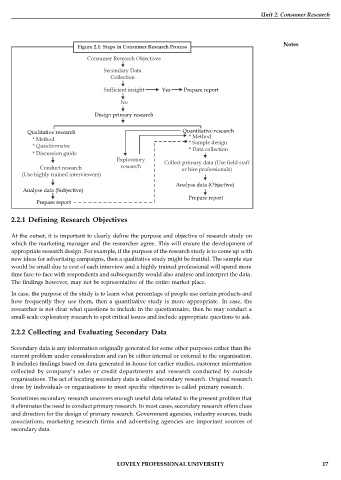
Figure 2.1: Steps in Consumer Research Process
Consumer Research Objectives
Secondary Data
Collection
Sufficient insight Yes Prepare report
No
Design primary research
Qualitative research Quantitative research
* Method
* Method * Sample design
* Questionnaire
* Data collection
* Discussion guide
Exploratory Collect primary data (Use field staff
Conduct research research or hire professionals)
(Use highly trained interviewers)
Analyse data (Objective)
Analyse data (Subjective)
Prepare report
Prepare report
2.2.1 Defining Research Objectives
At the outset, it is important to clearly define the purpose and objective of research study on
which the marketing manager and the researcher agree. This will ensure the development of
appropriate research design. For example, if the purpose of the research study is to come up with
new ideas for advertising campaigns, then a qualitative study might be fruitful. The sample size
would be small due to cost of each interview and a highly trained professional will spend more
time face-to-face with respondents and subsequently would also analyse and interpret the data.
The findings however, may not be representative of the entire market place.
In case, the purpose of the study is to learn what percentage of people use certain products and
how frequently they use them, then a quantitative study is more appropriate. In case, the
researcher is not clear what questions to include in the questionnaire, then he may conduct a
small-scale exploratory research to spot critical issues and include appropriate questions to ask.
2.2.2 Collecting and Evaluating Secondary Data
Secondary data is any information originally generated for some other purposes rather than the
current problem under consideration and can be either internal or external to the organisation.
It includes findings based on data generated in-house for earlier studies, customer information
collected by company’s sales or credit departments and research conducted by outside
organisations. The act of locating secondary data is called secondary research. Original research
done by individuals or organisations to meet specific objectives is called primary research.
Sometimes secondary research uncovers enough useful data related to the present problem that
it eliminates the need to conduct primary research. In most cases, secondary research offers clues
and direction for the design of primary research. Government agencies, industry sources, trade
associations, marketing research firms and advertising agencies are important sources of
secondary data.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 17