Page 55 - DMGT522_SERVICES MANAGEMENT
P. 55
Services Management
Notes and fiscal benefits play a major role in driving R&D investments towards these countries. MNCs
from developed nations look to expanding their R&D activities in these countries through
collaborative projects in areas such as electronics and telecommunications, software development,
hardware and product design and drug development. A White Paper on R&D prepared by
consultancy firm Deloitte in July 2011 estimates that more than 300 MNCs have set up R&D
centers in India. Service providers have outsourced R&D valued at about US$ 3.5 billion, and
MNC subsidiaries have off shored R&D valued at about US$ 6.5 billion to India in 2009. As per
the Global Competitiveness Report 2011-12 of the World Economic Forum, among BRICS nations
India is ranked below China and Brazil in terms of capacity for innovation but above China in
terms of the quality of scientific and research institutions and availability of scientists and
engineers. But India lags China in terms of company spending in R&D, university–industry
collaboration on R&D, and utility patents granted per million population (Table 2.9). This is
because the share of the private sector in R&D is still low at 0.25 per cent of GDP compared to 1.2
to 2 per cent in many developed and emerging economies. For GERD to increase significantly,
private-sector investment in R&D must be stepped up significantly over the Twelfth Plan period.
Budget 2011-12 enhanced the weighted deduction on payments made to National laboratories/
universities and institutes of technology for scientific research from 175 per cent to 200 per cent.
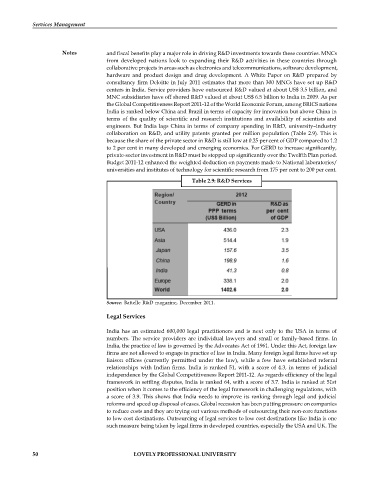
Table 2.9: R&D Services
Source: Battelle R&D magazine, December 2011.
Legal Services
India has an estimated 600,000 legal practitioners and is next only to the USA in terms of
numbers. The service providers are individual lawyers and small or family-based firms. In
India, the practice of law is governed by the Advocates Act of 1961. Under this Act, foreign law
firms are not allowed to engage in practice of law in India. Many foreign legal firms have set up
liaison offices (currently permitted under the law), while a few have established referral
relationships with Indian firms. India is ranked 51, with a score of 4.3, in terms of judicial
independence by the Global Competitiveness Report 2011-12. As regards efficiency of the legal
framework in settling disputes, India is ranked 64, with a score of 3.7. India is ranked at 51st
position when it comes to the efficiency of the legal framework in challenging regulations, with
a score of 3.9. This shows that India needs to improve its ranking through legal and judicial
reforms and speed up disposal of cases. Global recession has been putting pressure on companies
to reduce costs and they are trying out various methods of outsourcing their non-core functions
to low cost destinations. Outsourcing of legal services to low cost destinations like India is one
such measure being taken by legal firms in developed countries, especially the USA and UK. The
50 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY