Page 30 - DMGT546_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_PROCEDURE_AND_DOCUMENTATION
P. 30
Unit 2: Methods of Payment and Incoterms
The exporter can choose any mode of payments depending on risk perception, size of deal, Notes
importer creditworthiness and importer’s country economic situation.
In case of domestic business, a major factor that drives salesman decision criteria for realization
of payments is based on the buyer’s ability, willingness and honesty to make payment coupled
with the exporter’s trust on buyer. Usually, sales made in the domestic market are on open
account and in certain cases, can be on cash in advance. Such methods of payment to be used in
domestic market also depend on buyers and seller power to negotiate and the nature of
competition. For instance, monopoly conditions will favour the seller; and perfect competition
will favour the buyers. However, in case of international trade, the exporter has to take more
precautions, as some of the methods of payments used are unique and used usually in case of
international trade only. There are five basic methods of receiving payments from the importers
in international trade. In addition to these five, new adaptations in mode of payments have
evolved in today’s liberalised era, such as sales on consignment basis and electronic sales. The
various methods of payment have been ranked in order of being most secure for the exporter to
the least secure and vice versa for importer. The basic methods of payment are:
1. Cash in Advance
2. Letter of Credit
3. Document against Payments
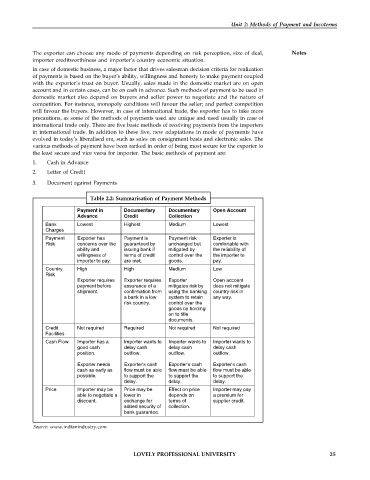
Table 2.2: Summarisation of Payment Methods
Payment in Documentary Documentary Open Account
Advance Credit Collection
Bank Lowest Highest Medium Lowest
Charges
Payment Exporter has Payment is Payment risk Exporter is
Risk concerns over the guaranteed by unchanged but comfortable with
ability and issuing bank if mitigated by the reliability of
willingness of terms of credit control over the the importer to
importer to pay. are met. goods. pay.
Country High High Medium Low
Risk
Exporter requires Exporter requires Exporter Open account
payment before assurance of a mitigates risk by does not mitigate
shipment. confirmation from using the banking country risk in
a bank in a low system to retain any way.
risk country. control over the
goods by holding
on to title
documents.
Credit Not required Required Not required Not required
Facilities
Cash Flow Importer has a Importer wants to Importer wants to Importer wants to
good cash delay cash delay cash delay cash
position. outflow. outflow. outflow.
Exporter needs Exporter's cash Exporter's cash Exporter's cash
cash as early as flow must be able flow must be able flow must be able
possible. to support the to support the to support the
delay. delay. delay.
Price Importer may be Price may be Effect on price Importer may pay
able to negotiate a lower in depends on a premium for
discount. exchange for terms of supplier credit.
added security of collection.
bank guarantee.
Source: www.indianindustry.com
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 25